Optimizing the Solvent Selection of the Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) Pomace: Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activity
- PMID: 38338617
- PMCID: PMC10855374
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13030482
Optimizing the Solvent Selection of the Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) Pomace: Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
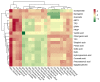
Sea buckthorn pomace (SBP) is a by-product of sea buckthorn processing that is rich in bioactive compounds. In this study, different active ingredients were extracted by using different solvents (water, methanol, ethanol, glycerol, ethyl acetate, and petroleum ether) combined with an ultrasonic assisted method. The correlation between the active ingredients and antioxidant properties of the extract was studied, which provided a research basis for the comprehensive utilization of SBP. This study revealed that the 75% ethanol extract had the highest total phenolic content (TPC) of 42.86 ± 0.73 mg GAE/g, while the 75% glycerol extract had the highest total flavonoid content (TFC) of 25.52 ± 1.35 mg RTE/g. The ethanol extract exhibited the strongest antioxidant activity at the same concentration compared with other solvents. The antioxidant activity of the ethanol, methanol, and glycerol extracts increased in a concentration-dependent manner. Thirteen phenolic compounds were detected in the SBP extracts using UPLC-MS/MS analysis. Notably, the 75% glycerol extract contained the highest concentration of all identified phenolic compounds, with rutin (192.21 ± 8.19 μg/g), epigallocatechin (105.49 ± 0.69 μg/g), and protocatechuic acid (27.9 ± 2.38 μg/g) being the most abundant. Flavonols were found to be the main phenolic substances in SBP. A strong correlation was observed between TPC and the antioxidant activities of SBP extracts. In conclusion, the choice of solvent significantly influences the active compounds and antioxidant activities of SBP extracts. SBP extracts are a valuable source of natural phenolics and antioxidants.
Keywords: UPLC-MS/MS; antioxidant activity; sea buckthorn pomace; solvent extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sun Z., Zhang G., Li X., Cui Q., Gong L., Tian Z. Non-Targeted Profiling of Sea Buckthorn Fruit Oil Fingerprints from 3 Regions and Study on Its Antioxidant Activity. [(accessed on 7 January 2024)];Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023 doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04744-y. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12010-023-04744-y. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

