Multiplexed Imaging Mass Cytometry Analysis in Preclinical Models of Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 38338669
- PMCID: PMC10855072
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25031389
Multiplexed Imaging Mass Cytometry Analysis in Preclinical Models of Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
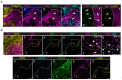
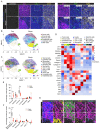
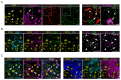
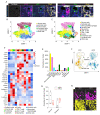
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most lethal cancers. PDAC is characterized by a complex tumor microenvironment (TME), that plays a pivotal role in disease progression and resistance to therapy. Investigating the spatial distribution and interaction of TME cells with the tumor is the basis for understanding the mechanisms underlying disease progression and represents a current challenge in PDAC research. Imaging mass cytometry (IMC) is the major multiplex imaging technology for the spatial analysis of tumor heterogeneity. However, there is a dearth of reports of multiplexed IMC panels for different preclinical mouse models, including pancreatic cancer. We addressed this gap by utilizing two preclinical models of PDAC: the genetically engineered, bearing KRAS-TP53 mutations in pancreatic cells, and the orthotopic, and developed a 28-marker panel for single-cell IMC analysis to assess the abundance, distribution and phenotypes of cells involved in PDAC progression and their reciprocal functional interactions. Herein, we provide an unprecedented definition of the distribution of TME cells in PDAC and compare the diversity between transplanted and genetic disease models. The results obtained represent an important and customizable tool for unraveling the complexities of PDAC and deciphering the mechanisms behind therapy resistance.
Keywords: PDAC; imaging mass cytometry; multiplexed imaging; pancreatic cancer; preclinical models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Panoramic tumor microenvironment in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Oct;47(5):1561-1578. doi: 10.1007/s13402-024-00970-6. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 39008192 Review.
-
Modeling pancreatic cancer in mice for experimental therapeutics.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Aug;1876(1):188554. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188554. Epub 2021 May 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33945847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the spatial distribution of extracellular adenosine revealed a myeloid-dependent immunosuppressive microenvironment in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Aug;11(8):e006457. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006457. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37553182 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative assessment of pancreatic cancer precursor lesions in IHC-stained tissue with a tissue image analysis platform.Lab Invest. 2016 Dec;96(12):1327-1336. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.111. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 27775692
-
Translating complexity and heterogeneity of pancreatic tumor: 3D in vitro to in vivo models.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Jul;174:265-293. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.04.018. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33895214 Review.
Cited by
-
Depicting the cellular complexity of pancreatic adenocarcinoma by Imaging Mass Cytometry: focus on cancer-associated fibroblasts.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 7;15:1472433. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1472433. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39575252 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Targeted Monoclonal IgA Antibodies Against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Cells. 2025 Apr 24;14(9):632. doi: 10.3390/cells14090632. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40358156 Free PMC article.
-
From surfing to diving into the tumor microenvironment through multiparametric imaging mass cytometry.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 11;16:1544844. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1544844. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40292277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of metal stable isotopes labeling and elemental mass spectrometry for biomacromolecule profiling.Biophys Rep. 2025 Apr 30;11(2):112-128. doi: 10.52601/bpr.2024.240039. Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40308936 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

