DNA Polymerase I Large Fragment from Deinococcus radiodurans, a Candidate for a Cutting-Edge Room-Temperature LAMP
- PMID: 38338670
- PMCID: PMC10855757
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25031392
DNA Polymerase I Large Fragment from Deinococcus radiodurans, a Candidate for a Cutting-Edge Room-Temperature LAMP
Abstract
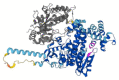
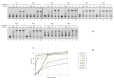
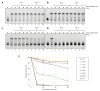
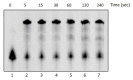
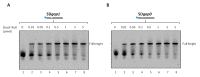
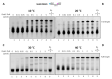
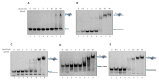
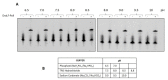
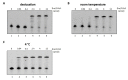
In recent years, the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) technique, designed for microbial pathogen detection, has acquired fundamental importance in the biomedical field, providing rapid and precise responses. However, it still has some drawbacks, mainly due to the need for a thermostatic block, necessary to reach 63 °C, which is the BstI DNA polymerase working temperature. Here, we report the identification and characterization of the DNA polymerase I Large Fragment from Deinococcus radiodurans (DraLF-PolI) that functions at room temperature and is resistant to various environmental stress conditions. We demonstrated that DraLF-PolI displays efficient catalytic activity over a wide range of temperatures and pH, maintains its activity even after storage under various stress conditions, including desiccation, and retains its strand-displacement activity required for isothermal amplification technology. All of these characteristics make DraLF-PolI an excellent candidate for a cutting-edge room-temperature LAMP that promises to be very useful for the rapid and simple detection of pathogens at the point of care.
Keywords: DNA polymerase; DNA replication; Deinococcus radiodurans; LAMP; extremophiles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
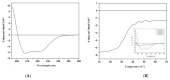
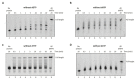
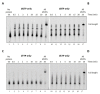
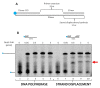

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

