Cancer Spheroids Embedded in Tissue-Engineered Skin Substitutes: A New Method to Study Tumorigenicity In Vivo
- PMID: 38338792
- PMCID: PMC10855415
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25031513
Cancer Spheroids Embedded in Tissue-Engineered Skin Substitutes: A New Method to Study Tumorigenicity In Vivo
Abstract
Tumorigenic assays are used during a clinical translation to detect the transformation potential of cell-based therapies. One of these in vivo assays is based on the separate injection of each cell type to be used in the clinical trial. However, the injection method requires many animals and several months to obtain useful results. In previous studies, we showed the potential of tissue-engineered skin substitutes (TESs) as a model for normal skin in which cancer cells can be included in vitro. Herein, we showed a new method to study tumorigenicity, using cancer spheroids that were embedded in TESs (cTES) and grafted onto athymic mice, and compared it with the commonly used cell injection assay. Tumors developed in both models, cancer cell injection and cTES grafting, but metastases were not detected at the time of sacrifice. Interestingly, the rate of tumor development was faster in cTESs than with the injection method. In conclusion, grafting TESs is a sensitive method to detect tumor cell growth with and could be developed as an alternative test for tumorigenicity.
Keywords: cancer spheroids; cell culture; grafting; skin; tissue engineering; tissue-engineered substitutes; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

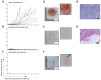

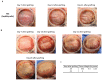
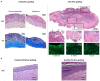
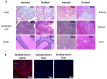
References
-
- Ito E., Miyagawa S., Takeda M., Kawamura A., Harada A., Iseoka H., Yajima S., Sougawa N., Mochizuki-Oda N., Yasuda S., et al. Tumorigenicity assay essential for facilitating safety studies of hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes for clinical application. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:1881. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38325-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- FDA . Characterization and Qualification of Cell Substrates and Other Biological Materials Used in the Production of Viral Vaccines for Infectious Disease Indications. Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research; Rockville, MA, USA: 2010.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

