In Vitro MRS of Cells Treated with Trastuzumab at 1.5 Tesla
- PMID: 38338997
- PMCID: PMC10855746
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25031719
In Vitro MRS of Cells Treated with Trastuzumab at 1.5 Tesla
Abstract
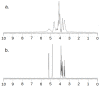
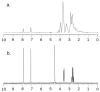
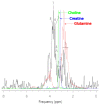
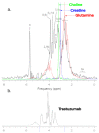
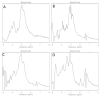
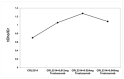
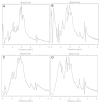
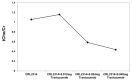
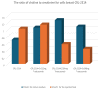
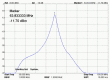
The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of Trastuzumab on the MCF-7 and CRL-2314 breast cancer cell lines. Additionally, an attempt was made to optimize magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) for cell culture studies, with particular emphasis on the impact of treatment with Trastuzumab. The research materials included MCF-7 and CRL-2314 breast cancer cell lines. The study examined the response of these cell lines to treatment with Trastuzumab. The clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, OPTIMA MR360 manufactured by GEMS, with a magnetic field induction of 1.5 T, was used. Due to the nature of the tested objects, their size and shape, it was necessary to design and manufacture additional receiving coils. They were used to image the tested cell cultures and record the spectroscopic signal. The spectra obtained by MRS were confirmed by NMR using a 300 MHz NMR Fourier 300 with the TopSpin 3.1 system from Bruker. The designed receiving coils allowed for conducting experiments with the cell lines in a satisfactory manner. These tests would not be possible using factory-delivered coils due to their parameters and the size of the test objects, whose volume did not exceed 1 mL. MRS studies revealed an increase in the metabolite at 1.9 ppm, which indicates the induction of histone acetylation. Changes in histone acetylation play a very important role in both cell development and differentiation processes. The use of Trastuzumab therapy in breast cancer cells increases the levels of acetylated histones. MRS studies and spectra obtained from the 300 MHz NMR system are consistent with the specificity inherent in both systems.
Keywords: MRS; Trastuzumab; breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Utility of 1.5 Tesla MRI Scanner in the Management of Small Sample Sizes Driven from 3D Breast Cell Culture.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 5;25(5):3009. doi: 10.3390/ijms25053009. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474256 Free PMC article.
-
An analytical study of Trastuzumab-dendrimer-fluorine drug delivery system in breast cancer therapy in vitro.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jan;133:111053. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111053. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33378959
-
Trastuzumab improves tumor perfusion and vascular delivery of cytotoxic therapy in a murine model of HER2+ breast cancer: preliminary results.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jan;155(2):273-84. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3680-8. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26791520 Free PMC article.
-
Development and applications of in vivo clinical magnetic resonance spectroscopy.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1996;65(1-2):45-81. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6107(96)00006-5. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 9029941 Review.
-
[(1)H magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) of the liver and hepatic malignant tumors at 3.0 Tesla].Radiologe. 2004 Dec;44(12):1192-6. doi: 10.1007/s00117-004-1136-3. Radiologe. 2004. PMID: 15549225 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Pure-Shift-Based Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for High-Resolution Studies of Biological Samples.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 25;25(9):4698. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094698. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Igarashi H., Takeda M., Natsumeda M., Fujii Y. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) No Shinkei Geka. 2021;49:438–444. - PubMed
-
- Wild C.P., Weiderpass E., Stewart B.W. World Cancer Report: Cancer Research for Cancer Prevention. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2020. [(accessed on 17 January 2022)]. Available online: http://publications.iarc.fr/586.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

