P2X7 Receptor-Induced Human Mast Cell Degranulation Is Enhanced by Interleukin 33
- PMID: 38339008
- PMCID: PMC10855801
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25031730
P2X7 Receptor-Induced Human Mast Cell Degranulation Is Enhanced by Interleukin 33
Abstract
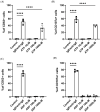
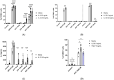
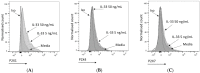
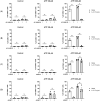
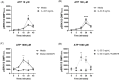
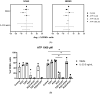
MCs are tissue-resident immune cells that strategically reside in barrier organs and respond effectively to a wide range of stimuli, such as IL-33, a mediator released upon epithelial damage. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) accumulates at sites of tissue injury and is known to modulate MC activities. This study investigated how an inflammatory tissue environment rich in IL-33 modulates the ATP-mediated activation of MCs. Human primary MCs primed with IL-33 displayed a strongly increased response to ATP but not ADP. This resulted in increased degranulation, IL-8 release, and pERK1/2 signalling. Such effects are unique to IL-33 stimulation and not shared by the epithelial alarmin, TSLP. MC exposure to IL-33 also increased membrane expression of purinergic and ATP-binding P2X receptors. The use of selective P2X receptor inhibitors identified P2X7 receptor as the key mediator of the enhanced ATP-induced ERK1/2 signalling and degranulation in IL-33-primed MCs. Whilst the inhibition of P2X1 and P2X4 receptors had no effect on MC degranulation, inhibiting these receptors together with P2X7 resulted in further decreased MC-mediated degranulation. These data therefore point toward the potential mechanisms by which IL-33 contributes to the modulation of ATP-mediated activation in human MCs.
Keywords: ATP; IL-33; P2X1; P2X4; P2X7; mast cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. K.A. is an employee of GSK; however, no conflicts of interest in relation to this manuscript have arisen.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Divergent regulatory roles of extracellular ATP in the degranulation response of mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Feb;43:99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.12.014. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27988461
-
ATP/IL-33-triggered hyperactivation of mast cells results in an amplified production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and eicosanoids.Immunology. 2021 Nov;164(3):541-554. doi: 10.1111/imm.13386. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 34142370 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular ATP Augments Antigen-Induced Murine Mast Cell Degranulation and Allergic Responses via P2X4 Receptor Activation.J Immunol. 2020 Jun 15;204(12):3077-3085. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900954. Epub 2020 May 1. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32358018
-
Purinergic regulation of mast cell function: P2X4 receptor-mediated enhancement of allergic responses.J Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Oct;150(2):94-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2022.07.005. Epub 2022 Aug 8. J Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36055757 Review.
-
Structural and Functional Features of the P2X4 Receptor: An Immunological Perspective.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 25;12:645834. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.645834. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33897694 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive insights into potential roles of purinergic P2 receptors on diseases: Signaling pathways involved and potential therapeutics.J Adv Res. 2025 Mar;69:427-448. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.03.027. Epub 2024 Mar 31. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38565403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

