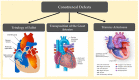
In-Depth Genomic Analysis: The New Challenge in Congenital Heart Disease
- PMID: 38339013
- PMCID: PMC10855915
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25031734
In-Depth Genomic Analysis: The New Challenge in Congenital Heart Disease
Abstract
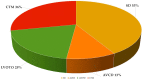
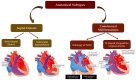
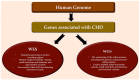
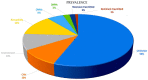
The use of next-generation sequencing has provided new insights into the causes and mechanisms of congenital heart disease (CHD). Examinations of the whole exome sequence have detected detrimental gene variations modifying single or contiguous nucleotides, which are characterised as pathogenic based on statistical assessments of families and correlations with congenital heart disease, elevated expression during heart development, and reductions in harmful protein-coding mutations in the general population. Patients with CHD and extracardiac abnormalities are enriched for gene classes meeting these criteria, supporting a common set of pathways in the organogenesis of CHDs. Single-cell transcriptomics data have revealed the expression of genes associated with CHD in specific cell types, and emerging evidence suggests that genetic mutations disrupt multicellular genes essential for cardiogenesis. Metrics and units are being tracked in whole-genome sequencing studies.
Keywords: congenital heart disease; copy number variants; de novo mutations; deletion; first heart field; gene variants; loss-of-function variant; second heart field; whole-exome sequencing; whole-genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dilli D., Akduman H., Zenciroğlu A., Çetinkaya M., Okur N., Turan Ö., Özlü F., Çalkavur Ş., Demirel G., Koksal N., et al. Neonatal Outcomes of Critical Congenital Heart Defects: A Multicenter Epidemiological Study of Turkish Neonatal Society: Neonatal Outcomes of CCHD. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2024;45:257–271. doi: 10.1007/s00246-023-03362-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hossin M.Z., de la Cruz L.F., McKay K.A., Oberlander T.F., Sandström A., Razaz N. Association of pre-existing maternal cardiovascular diseases with neurodevelopmental disorders in offspring: A cohort study in Sweden and British Columbia, Canada. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2023:dyad184. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyad184. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakker M.K., Bergman J.E.H., Krikov S., Amar E., Cocchi G., Cragan J., de Walle H.E.K., Gatt M., Groisman B., Liu S., et al. Prenatal diagnosis and prevalence of critical congenital heart defects: An international retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e028139. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028139. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

