From Acute to Chronic: Unraveling the Pathophysiological Mechanisms of the Progression from Acute Kidney Injury to Acute Kidney Disease to Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 38339031
- PMCID: PMC10855633
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25031755
From Acute to Chronic: Unraveling the Pathophysiological Mechanisms of the Progression from Acute Kidney Injury to Acute Kidney Disease to Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
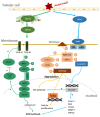
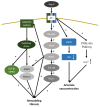
This article provides a thorough overview of the biomarkers, pathophysiology, and molecular pathways involved in the transition from acute kidney injury (AKI) and acute kidney disease (AKD) to chronic kidney disease (CKD). It categorizes the biomarkers of AKI into stress, damage, and functional markers, highlighting their importance in early detection, prognosis, and clinical applications. This review also highlights the links between renal injury and the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying AKI and AKD, including renal hypoperfusion, sepsis, nephrotoxicity, and immune responses. In addition, various molecules play pivotal roles in inflammation and hypoxia, triggering maladaptive repair, mitochondrial dysfunction, immune system reactions, and the cellular senescence of renal cells. Key signaling pathways, such as Wnt/β-catenin, TGF-β/SMAD, and Hippo/YAP/TAZ, promote fibrosis and impact renal function. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) triggers a cascade leading to renal fibrosis, with aldosterone exacerbating the oxidative stress and cellular changes that promote fibrosis. The clinical evidence suggests that RAS inhibitors may protect against CKD progression, especially post-AKI, though more extensive trials are needed to confirm their full impact.
Keywords: acute kidney disease; acute kidney injury; biomarker; chronic kidney disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chawla L.S., Bellomo R., Bihorac A., Goldstein S.L., Siew E.D., Bagshaw S.M., Bittleman D., Cruz D., Endre Z., Fitzgerald R.L., et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: Consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017;13:241–257. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Levey A.S., Eckardt K.-U., Tsukamoto Y., Levin A., Coresh J., Rossert J., Zeeuw D.D., Hostetter T.H., Lameire N., Eknoyan G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: A position statement from kidney disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Kidney Int. 2005;67:2089–2100. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00365.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lameire N.H., Levin A., Kellum J.A., Cheung M., Jadoul M., Winkelmayer W.C., Stevens P.E., Caskey F.J., Farmer C.K., Fuentes A.F., et al. Harmonizing acute and chronic kidney disease definition and classification: Report of a kidney disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Consensus Conference. Kidney Int. 2021;100:516–526. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.06.028. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

