Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications of Human Pericyte-like Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in an In Vitro Model of Diabetic Retinopathy
- PMID: 38339053
- PMCID: PMC10855418
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25031774
Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications of Human Pericyte-like Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in an In Vitro Model of Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
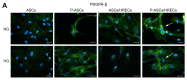
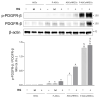
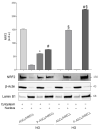
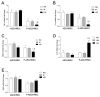
The blood-retinal barrier (BRB) is strongly compromised in diabetic retinopathy (DR) due to the detachment of pericytes (PCs) from retinal microvessels, resulting in increased permeability and impairment of the BRB. Western blots, immunofluorescence and ELISA were performed on adipose mesenchymal stem cells (ASCs) and pericyte-like (P)-ASCs by co-cultured human retinal endothelial cells (HRECs) under hyperglycemic conditions (HG), as a model of DR. Our results demonstrated that: (a) platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) and its activated form were more highly expressed in monocultured P-ASCs than in ASCs, and this expression increased when co-cultured with HRECs under high glucose conditions (HG); (b) the transcription factor Nrf2 was more expressed in the cytoplasmic fraction of ASCs and in the P-ASC nuclear fraction, under normal glucose and, even more, under HG conditions; (c) cytosolic phospholipase A2 activity and prostaglandin E2 release, stimulated by HG, were significantly reduced in P-ASCs co-cultured with HRECs; (d) HO-1 protein content was significantly higher in HG-P-ASCs/HRECs than P-ASCs/HRECs; and (e) VEGF-A levels in media from HG-co-cultures were reduced in P-ASCs/HRECs with respect to ASCs/HRECs. The data obtained highlighted the potential of autologous differentiated ASCs in future clinical applications based on cell therapy to counteract the damage induced by DR.
Keywords: adipose mesenchymal stem cells; blood–retinal barrier; cell-based therapy; cytosolic phospholipase A2; diabetic retinopathy; human retinal endothelial cells; hyperglycemia; inflammation; pericyte-like differentiation; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

