Exploring Novel Sensor Design Ideas through Concentration-Induced Conformational Changes in PEG Single Chains
- PMID: 38339600
- PMCID: PMC10856974
- DOI: 10.3390/s24030883
Exploring Novel Sensor Design Ideas through Concentration-Induced Conformational Changes in PEG Single Chains
Abstract
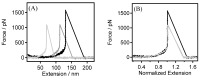
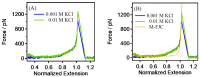
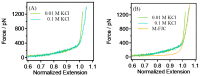
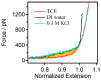
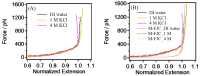
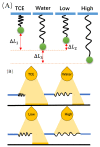
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is an artificial polymer with good biocompatibility and a low cost, which has a wide range of applications. In this study, the dynamic response of PEG single chains to different ion concentrations was investigated from a microscopic point of view based on single-molecule force spectroscopy, revealing unique interactions that go beyond the traditional sensor-design paradigm. Under low concentrations of potassium chloride, PEG single chains exhibit a gradual reduction in rigidity, while, conversely, high concentrations induce a progressive increase in rigidity. This dichotomy serves as the cornerstone for a profound understanding of PEG conformational dynamics under diverse ion environments. Capitalizing on the remarkable sensitivity of PEG single chains to ion concentration shifts, we introduce innovative sensor-design ideas. Rooted in the adaptive nature of PEG single chains, these sensor designs extend beyond the traditional applications, promising advancements in environmental monitoring, healthcare, and materials science.
Keywords: PEG; ion concentration; single-chain rigidity; single-molecule force spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting the Miscibility and Rigidity of Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/Polyethylene Glycol Blends via Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Macromolecules. 2020 May 26;53(10):3643-3654. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00110. Epub 2020 May 12. Macromolecules. 2020. PMID: 32831403 Free PMC article.
-
Binding characteristics between polyethylene glycol (PEG) and proteins in aqueous solution.J Mater Chem B. 2014 May 28;2(20):2983-2992. doi: 10.1039/c4tb00253a. Epub 2014 Apr 8. J Mater Chem B. 2014. PMID: 32261674
-
Development and application of an excitation ratiometric optical pH sensor for bioprocess monitoring.Biotechnol Prog. 2008 Nov-Dec;24(6):1393-401. doi: 10.1002/btpr.66. Biotechnol Prog. 2008. PMID: 19194954
-
Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: a review.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013 Nov;85(3 Pt A):427-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013. PMID: 23872180 Review.
-
Effect of polyethylene glycol on polysaccharides: From molecular modification, composite matrixes, synergetic properties to embeddable application in food fields.Carbohydr Polym. 2024 Mar 1;327:121647. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121647. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Carbohydr Polym. 2024. PMID: 38171672 Review.
References
-
- Erçarikci E., Dagci Kiransan K., Topçu E. A Flexible Graphene Paper Electrochemical Sensor with Electrodeposited Ag and Ni Nanoparticles for H2O2 Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2023;23:7087–7094. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3246380. - DOI
-
- Ko Y., Jeong H.Y., Kwon G., Kim D., Lee C., You J. pH-responsive polyaniline/polyethylene glycol composite arrays for colorimetric sensor application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020;305:127447. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.127447. - DOI
-
- Cao Y., Weng M.M., Mahmoud M.H.H., Elnaggar A.Y., Zhang L., El Azab I.H., Chen Y., Huang M.N., Huang J.T., Sheng X.X. Flame-retardant and leakage-proof phase change composites based on MXene/polyimide aerogels toward solar thermal energy harvesting. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022;5:1253–1267. doi: 10.1007/s42114-022-00504-4. - DOI
-
- Redij R., Kaur A., Muddaloor P., Sethi A.K., Aedma K., Rajagopal A., Gopalakrishnan K., Yadav A., Damani D.N., Chedid V.G., et al. Practicing Digital Gastroenterology through Phonoenterography Leveraging Artificial Intelligence: Future Perspectives Using Microwave Systems. Sensors. 2023;23:2302. doi: 10.3390/s23042302. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

