Fluorinated Pharmaceutical and Pesticide Photolysis: Investigating Reactivity and Identifying Fluorinated Products by Combining Computational Chemistry,19F NMR, and Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 38340057
- PMCID: PMC10883306
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.3c09341
Fluorinated Pharmaceutical and Pesticide Photolysis: Investigating Reactivity and Identifying Fluorinated Products by Combining Computational Chemistry,19F NMR, and Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
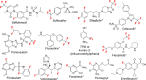
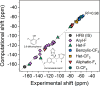
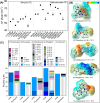
Fluorinated breakdown products from photolysis of pharmaceuticals and pesticides are of environmental concern due to their potential persistence and toxicity. While mass spectrometry workflows have been shown to be useful in identifying products, they fall short for fluorinated products and may miss up to 90% of products. Studies have shown that 19F NMR measurements assist in identifying and quantifying reaction products, but this protocol can be further developed by incorporating computations. Density functional theory was used to compute 19F NMR shifts for parent and product structures in photolysis reactions. Computations predicted NMR spectra of compounds with an R2 of 0.98. Computed shifts for several isolated product structures from LC-HRMS matched the experimental shifts with <0.7 ppm error. Multiple products including products that share the same shift that were not previously reported were identified and quantified using computational shifts, including aliphatic products in the range of -80 to -88 ppm. Thus, photolysis of fluorinated pharmaceuticals and pesticides can result in compounds that are polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS), including aliphatic-CF3 or vinyl-CF2 products derived from heteroaromatic-CF3 groups. C-F bond-breaking enthalpies and electron densities around the fluorine motifs agreed well with the experimentally observed defluorination of CF3 groups. Combining experimental-computational 19F NMR allows quantification of products identified via LC-HRMS without the need for authentic standards. These results have applications for studies of environmental fate and analysis of fluorinated pharmaceuticals and pesticides in development.
Keywords: 19F NMR; PFAS; density functional theory; direct photolysis; photoproducts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Photolysis Products of Fluorinated Pharmaceuticals: A Combined Fluorine Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry Approach.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2024 Nov;43(11):2285-2296. doi: 10.1002/etc.5773. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2024. PMID: 37861370
-
Wavelength-Dependent UV-LED Photolysis of Fluorinated Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals.Environ Sci Technol. 2023 Apr 4;57(13):5327-5336. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c00627. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Environ Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 36962003
-
Tracking Fluorine during Aqueous Photolysis and Advanced UV Treatment of Fluorinated Phenols and Pharmaceuticals Using a Combined 19F-NMR, Chromatography, and Mass Spectrometry Approach.ACS Environ Au. 2022 Feb 14;2(3):242-252. doi: 10.1021/acsenvironau.1c00057. eCollection 2022 May 18. ACS Environ Au. 2022. PMID: 37102144 Free PMC article.
-
Practical synthesis of fluorine-containing α- and β-amino acids: recipes from Kiev, Ukraine.Future Med Chem. 2009 Aug;1(5):793-819. doi: 10.4155/fmc.09.70. Future Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 21426081 Review.
-
19F Solid-state NMR characterization of pharmaceutical solids.Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2022 Aug;120:101796. doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2022.101796. Epub 2022 May 25. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2022. PMID: 35688018 Review.
References
-
- Fujiwara T.; O’Hagan D. Successful Fluorine-Containing Herbicide Agrochemicals. J. Fluor. Chem. 2014, 167, 16–29. 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2014.06.014. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

