Federated machine learning in healthcare: A systematic review on clinical applications and technical architecture
- PMID: 38340728
- PMCID: PMC10897620
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101419
Federated machine learning in healthcare: A systematic review on clinical applications and technical architecture
Erratum in
-
Federated machine learning in healthcare: A systematic review on clinical applications and technical architecture.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Mar 19;5(3):101481. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101481. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 38508145 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
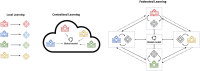
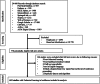
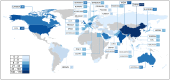
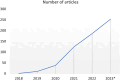
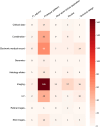
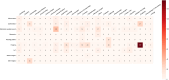
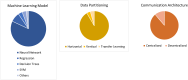
Federated learning (FL) is a distributed machine learning framework that is gaining traction in view of increasing health data privacy protection needs. By conducting a systematic review of FL applications in healthcare, we identify relevant articles in scientific, engineering, and medical journals in English up to August 31st, 2023. Out of a total of 22,693 articles under review, 612 articles are included in the final analysis. The majority of articles are proof-of-concepts studies, and only 5.2% are studies with real-life application of FL. Radiology and internal medicine are the most common specialties involved in FL. FL is robust to a variety of machine learning models and data types, with neural networks and medical imaging being the most common, respectively. We highlight the need to address the barriers to clinical translation and to assess its real-world impact in this new digital data-driven healthcare scene.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; federated learning; healthcare; systematic review.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.S.W.T. holds a patent on a deep learning system for detection of retinal diseases and co-founded and holds equity in EyRIS Singapore.
Figures
References
-
- Sheller M.J., Edwards B., Reina G.A., Martin J., Pati S., Kotrotsou A., Milchenko M., Xu W., Marcus D., Colen R.R., Bakas S. Federated learning in medicine: facilitating multi-institutional collaborations without sharing patient data. Sci. Rep. 2020;10 doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69250-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McMahan HB, Moore E, Ramage D, Hampson S, y Arcas BA. Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data.arxiv Preprint at: Published online January 26, 2023. Accessed November 17, 2023. http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.05629
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

