GPX3 supports ovarian cancer tumor progression in vivo and promotes expression of GDF15
- PMID: 38342006
- PMCID: PMC11179984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2024.02.004
GPX3 supports ovarian cancer tumor progression in vivo and promotes expression of GDF15
Abstract
Objective: We previously reported that high expression of the extracellular glutathione peroxidase GPX3 is associated with poor patient outcome in ovarian serous adenocarcinomas, and that GPX3 protects ovarian cancer cells from oxidative stress in culture. Here we tested if GPX3 is necessary for tumor establishment in vivo and to identify novel downstream mediators of GPX3's pro-tumorigenic function.
Methods: GPX3 was knocked-down in ID8 ovarian cancer cells by shRNA to test the role of GPX3 in tumor establishment using a syngeneic IP xenograft model. RNA sequencing analysis was carried out in OVCAR3 cells following shRNA-mediated GPX3 knock-down to identify GPX3-dependent gene expression signatures.
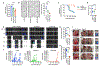
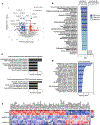
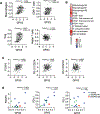
Results: GPX3 knock-down abrogated clonogenicity and intraperitoneal tumor development in vivo, and the effects were dependent on the level of GPX3 knock-down. RNA sequencing showed that loss of GPX3 leads to decreased gene expression patterns related to pro-tumorigenic signaling pathways. Validation studies identified GDF15 as strongly dependent on GPX3. GDF15, a member of the TGF-β growth factor family, has known oncogenic and immune modulatory activities. Similarly, GPX3 expression positively correlated with pro-tumor immune cell signatures, including regulatory T-cell and macrophage infiltration, and displayed significant correlation with PD-L1 expression.
Conclusions: We show for the first time that tumor produced GPX3 is necessary for ovarian cancer growth in vivo and that it regulates expression of GDF15. The immune profile associated with GPX3 expression in serous ovarian tumors suggests that GPX3 may be an alternate marker of ovarian tumors susceptible to immune check-point inhibitors.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; GDF15; GPX3; Metabolism; Ovarian cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
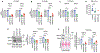
Update of
-
GPX3 supports ovarian cancer tumor progression in vivo and promotes expression of GDF15.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 29:2024.01.24.577037. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.24.577037. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Gynecol Oncol. 2024 Jun;185:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2024.02.004. PMID: 38352432 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, and Jemal A (2022) Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 72, 7–33 - PubMed
-
- Kim YS, Gupta Vallur P, Jones VM, Worley BL, Shimko S, Shin DH, Crawford LC, Chen CW, Aird KM, Abraham T, Shepherd TG, Warrick JI, Lee NY, Phaeton R, Mythreye K, and Hempel N (2020) Context-dependent activation of SIRT3 is necessary for anchorage-independent survival and metastasis of ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene 39, 1619–1633 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Worley BL, Kim YS, Mardini J, Zaman R, Leon KE, Vallur PG, Nduwumwami A, Warrick JI, Timmins PF, Kesterson JP, Phaeton R, Lee NY, Walter V, Endres L, Mythreye K, Aird KM, and Hempel N (2019) GPx3 supports ovarian cancer progression by manipulating the extracellular redox environment. Redox Biol 25, 101051. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

