Tumefactive multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 38343475
- PMCID: PMC10857543
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2023.2289301
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis
Abstract
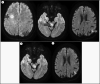
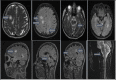
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis (MS) is a subtype of atypical and rare MS that presents with tumor-like lesions in the central nervous system. The lesions may demonstrate a mass effect, edema, with ring enhancement. They can be mistaken for brain tumors or brain abscesses radiologically and clinically. Here we describe an instructive case of a 55-year-old woman with tumefactive MS who presented with occasional numbness in her right arm and leg, headache, thought confusion, and blurred vision for 2 years.
Keywords: Abscess; demyelinating; tumor.
Copyright © 2023 Baylor University Medical Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no funding or conflicts of interest. The patient provided consent for this case report to be published.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
