Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: Cytologic-histologic correlation study and evaluation of the cytologic accuracy in identifying high-grade dysplasia/invasive adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38343764
- PMCID: PMC10858787
- DOI: 10.25259/Cytojournal_71_2023
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: Cytologic-histologic correlation study and evaluation of the cytologic accuracy in identifying high-grade dysplasia/invasive adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Objective: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) may be associated with invasive adenocarcinoma, low-grade dysplasia (LGD), or high-grade dysplasia (HGD). We aimed to review the cytologic-histologic correlation of cases with a histologic diagnosis of IPMN.
Material and methods: A database search (January 2010-January 2021) was performed for resected IPMNs with preceding endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (FNA). Cytology slides were reviewed for the presence of benign, atypical, or malignant cells, and necrosis. Histologically, IPMNs were classified as benign (LGD) or malignant (HGD or adenocarcinoma).
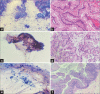
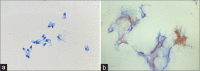
Results: There were 41 patients with IPMN; 24 malignant and 17 benign. Sixteen of the 24 malignant IPMNs were accurately classified as malignant on cytology. There were eight false negatives and one false positive. Cytology yielded a sensitivity of 67% and a specificity of 94%. Among the 16 true positives with FNA diagnosis of adenocarcinoma, seven were IPMNs with HGD, and nine had invasive adenocarcinomas on histology. Cellular morphology and absence or presence of necrosis did not help distinguish HGD from adenocarcinoma on cytology (P > 0.5). Sampling errors and interpretative errors resulted in false-negative cases. Cytology yielded diagnoses related to IPMN in 73% of cases (30/41) and lack of identification of mucinous cells/mucinous background resulted in interpretative errors (9).
Conclusion: This study shows that there is a good correlation between cytopathology and surgical pathology diagnoses of IPMNs and that cytology is mostly able to recognize IPMN with HGD/adenocarcinoma. However, heterogeneity in areas of IPMN with HGD/adenocarcinoma may result in sampling errors yielding false-negative cases. Mucinous cells/background should raise the suspicion of IPMN on cytology, even when no neoplastic epithelium is present for the evaluation of dysplasia.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma; Fine-needle aspiration; High-grade dysplasia; Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; Pancreas.
© 2024 Cytopathology Foundation Inc, Published by Scientific Scholar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytologic Evaluation of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm and Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms of Pancreas.Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 Sep 8;154(4):559-570. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa079. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32589187
-
MUC2 expression and prevalence of high-grade dysplasia and invasive carcinoma in mixed-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas.Pancreatology. 2013 Nov-Dec;13(6):583-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2013.08.007. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Pancreatology. 2013. PMID: 24280573
-
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. A study of 8 cases.JOP. 2007 Nov 9;8(6):715-24. JOP. 2007. PMID: 17993724
-
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: Cytomorphology, imaging, molecular profile, and prognosis.Cytopathology. 2021 Jul;32(4):397-406. doi: 10.1111/cyt.12973. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Cytopathology. 2021. PMID: 33792980 Review.
-
Acute pancreatitis in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: a single-center retrospective cohort study with systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Dec 1;23(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02972-4. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 38041073 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances in Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Based Diagnosis of Pancreatic Lesions: Narrative Review.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 7;17(2):172. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020172. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Digestive system tumours. 5th ed. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019. WHO classification of tumours.
-
- Expertpath Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. Available from: https://app.expertpath.com/document/intraductal-papillary-mucinous-neo-/... [Last accessed on 2022 Aug 21]
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
