Change in Achilles Tendon Length after Walking on Treadmill with Gradient
- PMID: 38343876
- PMCID: PMC10853016
- DOI: 10.2490/prm.20240006
Change in Achilles Tendon Length after Walking on Treadmill with Gradient
Abstract
Objectives: Improving ankle joint contracture is important because stiffness in ankle dorsiflexion can lead to pain, especially when weight-bearing during walking, which tends to concentrate on the forefoot. We hypothesized that the contraction of the gastrocnemius muscle in ankle dorsiflexion would increase the Achilles tendon length and improve the dorsiflexion range of motion. We evaluated the effects of walking with and without a gradient on Achilles tendon length.
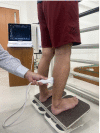
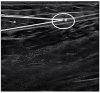
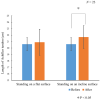
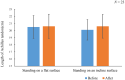
Methods: This study included 23 men who underwent ultrasound imaging to measure the Achilles tendon length while they stood on an inclined table adjusted according to the dorsiflexion angle. Treadmill walking was performed for 10 min with a 10° incline (gradient condition) or without gradient (level condition). The measurements were compared using a paired t-test.
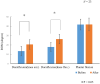
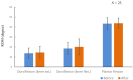
Results: In the gradient condition, the range of motion for ankle dorsiflexion was significantly increased after the intervention. In the gradient condition, the Achilles tendon length while standing on an inclined surface was significantly increased after the intervention.
Conclusions: Walking under gradient conditions led to the extension of the Achilles tendon in the ankle dorsiflexion position. This was accompanied by contraction of the gastrocnemius muscle, resulting in lengthening of the Achilles tendon. This finding suggests that such interventions may have clinical applications.
Keywords: Achilles tendon; treadmill walking; ultrasound imaging device.
2024 The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lv ML,Zhang H,Chen L,Liu Y,Wang F,Wong DW,Sun L,Ni M: Finite element method based parametric study of Gastrocnemius-soleus recession: implications to the treatment of midfoot-forefoot overload syndrome. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2021;24:913–921. 10.1080/10255842.2020.1858817 - DOI - PubMed

