Real-World Safety of TwinRab, the World's First Novel Cocktail of Rabies Monoclonal Antibodies, in a Clinical Setting
- PMID: 38344519
- PMCID: PMC10859109
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.52163
Real-World Safety of TwinRab, the World's First Novel Cocktail of Rabies Monoclonal Antibodies, in a Clinical Setting
Abstract
Objectives: Every year, 18,000-20,000 people die from rabies in India, with children younger than the age of 15 accounting for 30%-60% of all cases. Wound cleaning, vaccination, and rabies immunoglobulin (RIG) administration are all part of treatment. TwinRabTM, a unique combination of two monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), docaravimab and miromavimab, effectively neutralizes rabies and rabies-like viruses. We conducted this study to evaluate the safety of the cocktail in patients infected with category-III animal bites according to WHO guidelines.
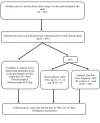
Methods: This open-label observational study was conducted in patients with WHO category-III animal bites by suspected rabid animals. All participants were screened, enrolled, and were administered the TwinRabTM manufactured by Zydus Lifesciences Ltd. at the rate of 40 IU/kg by infiltration in and around the wound along with anti-rabies vaccine (ARVs). Participants were assessed at various intervals, and any adverse events (AEs) were documented and reported to the sponsor within 24 hours.
Result: The study enrolled 401 participants, 55.61% (n = 223) male, whose median age was 34 years. Adults made up 69.83% (n = 280) of the participants. The most exposed sites were the lower parts of the body (60.6%, n = 243); 99.75% (n = 400) of the population showed normal cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and central nervous systems. After seven days of the last postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) dose, 9.98% of the total study population experienced 80 mild local solicited AEs and were assessed and treated.
Conclusion: The study concluded that TwinRabTM when given in a 40 IU/kg dose with Essen or the updated Thai Red Cross Vaccine regimen, provides safe and effective rabies prophylaxis in WHO category III patients exposed to suspected rabied animal bites.
Keywords: adverse events; post-exposure prophylaxis; rabies; safety assessment; twinrabtm.
Copyright © 2024, Manna et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared financial relationships, which are detailed in the next section.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing the Safety of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail for Postexposure Prophylaxis in Category III Animal Exposures.Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2024 Jul-Sep;14(3):193-198. doi: 10.4103/ijabmr.ijabmr_281_24. Epub 2024 Aug 24. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39310081 Free PMC article.
-
Safety assessment of the world's first novel cocktail of two monoclonal antibodies in WHO category-III animal-bite patients.J Family Med Prim Care. 2024 Oct;13(10):4493-4498. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_377_24. Epub 2024 Oct 18. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 39629371 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Marketing Surveillance of the World's First Novel Cocktail of Rabies Monoclonal Antibodies: TwinRab™ in Real \-World Setting.Indian J Community Med. 2024 Mar-Apr;49(2):443-447. doi: 10.4103/ijcm.ijcm_562_23. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Indian J Community Med. 2024. PMID: 38665446 Free PMC article.
-
A Phase 3, Randomized, Open-label, Noninferiority Trial Evaluating Anti-Rabies Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail (TwinrabTM) Against Human Rabies Immunoglobulin (HRIG).Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Nov 2;73(9):e2722-e2728. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa779. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 32556113 Clinical Trial.
-
Time to Revise the WHO Categories for Severe Rabies Virus Exposures-Category IV?Viruses. 2022 May 22;14(5):1111. doi: 10.3390/v14051111. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35632852 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Safety and tolerability of a novel monoclonal antibody cocktail for rabies post-exposure prophylaxis.NPJ Vaccines. 2025 May 21;10(1):102. doi: 10.1038/s41541-025-01109-w. NPJ Vaccines. 2025. PMID: 40399323 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Safety of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail for Postexposure Prophylaxis in Category III Animal Exposures.Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2024 Jul-Sep;14(3):193-198. doi: 10.4103/ijabmr.ijabmr_281_24. Epub 2024 Aug 24. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39310081 Free PMC article.
-
Safety assessment of the world's first novel cocktail of two monoclonal antibodies in WHO category-III animal-bite patients.J Family Med Prim Care. 2024 Oct;13(10):4493-4498. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_377_24. Epub 2024 Oct 18. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 39629371 Free PMC article.
-
Safety Evaluation of the Novel Cocktail of Monoclonal Antibodies for Postexposure Prophylaxis in Category III Animal Exposures.J Glob Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 18;16(4):140-144. doi: 10.4103/jgid.jgid_71_24. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. J Glob Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39886089 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends in anti-rabies virus monoclonal antibody: A bibliometric analysis.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2508559. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2508559. Epub 2025 May 26. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40418207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2013. WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies: WHO TRS N°982.
-
- New global strategic plan to eliminate animal-mediated rabies by 2030. Minghui R, Stone M, Semedo MH, Nel L. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/langlo/article/PIIS2214-109X(18)30302... Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6:828. - PubMed
-
- Rabies. [ Nov; 2023 ]. 2023. https://www.who.int/health-topics/rabies#tab=tab_1 https://www.who.int/health-topics/rabies#tab=tab_1
-
- Current rabies vaccines and prophylaxis schedules: preventing rabies before and after exposure. Warrell MJ. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/searo/india/health-topic-pdf/pep.... Travel Med Infect Dis. 2012;10:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Developments in rabies vaccines. Hicks DJ, Fooks AR, Johnson N. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22861358/ Clin Exp Immunol. 2012;169:199–204. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous