The Synthesis, Characterization, and Assessment of Antibacterial Properties of an Orthodontic Adhesive Containing Cerium-Substituted Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 38344531
- PMCID: PMC10859175
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.52177
The Synthesis, Characterization, and Assessment of Antibacterial Properties of an Orthodontic Adhesive Containing Cerium-Substituted Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
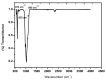
Introduction White spot lesions (WSLs) are early enamel caries lesions often seen in individuals receiving fixed orthodontic treatment. These lesions occur due to the buildup of plaque and the colonization of bacteria. WSL formation can be prevented by adequate oral hygiene measures and by the incorporation of antimicrobial nanoparticles (NPs) in orthodontic appliances and bonding systems. The aim of this research was to synthesize cerium-substituted hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (Ce-HAp NPs), characterize them, and assess their antimicrobial activity. Materials and methods This in vitro investigation involved the preparation of Ce-HAp NPs using the co-precipitation method, followed by their characterization using scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray (EDAX), and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR). The NPs were prepared and subsequently added to an orthodontic adhesive. Antibacterial testing was conducted using the disc diffusion method against common oral pathogens (Staphylococcus aureus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, and Streptococcus mutans). The zones of inhibition were measured for two different concentrations of the adhesive. Results The Ce-HAp NPs were successfully prepared and had an irregular agglomerated shape, measuring 63 nm in size. The major characteristic chemical groups of Ce-HAp were PO43-, OH-, and CO32-, and it was confirmed by the FTIR spectrum. The EDAX results of the synthesized NPs showed theoretical weight percentages (Wt%) of O, 52.6%; Ca, 20.9%; P, 11.8%; C, 10.3%; and Ce, 4.3%. A higher concentration of 40 µg/mL (30 mm for S. aureus and L. acidophilus and 25 mm for S. mutans) showed good antibacterial activity against the tested bacterial strains, compared to control antibiotics. Conclusion Cerium oxide (CeO2)-HAp NPs were prepared and incorporated into an orthodontic adhesive. The prepared adhesive exhibited effective antibacterial activity against prevalent oral pathogens.
Keywords: antibacterial activity; cerium; dental; hydroxyapatite; nanoparticles; orthodontic adhesives.
Copyright © 2024, Singh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
I have applied for a provisional patent for the obtained product to be put to use in future biomedicine.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Preparation and Assessment of Antimicrobial Effect of Strontium and Copper Co-substituted Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticle-Incorporated Orthodontic Composite: A Preliminary In Vitro Study.Cureus. 2023 Oct 22;15(10):e47495. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47495. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021789 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of a conventional orthodontic composite containing silver/hydroxyapatite nanoparticles.Prog Orthod. 2016 Dec;17(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s40510-016-0153-x. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Prog Orthod. 2016. PMID: 27819127 Free PMC article.
-
Shear bond strength, adhesive remnant index, and anti-biofilm effects of a photoexcited modified orthodontic adhesive containing curcumin doped poly lactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticles: An ex-vivo biofilm model of S. mutans on the enamel slab bonded brackets.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2020 Jun;30:101674. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.101674. Epub 2020 Jan 26. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2020. PMID: 31996322
-
Visible light-activated curcumin-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles integrated into orthodontic adhesive on Micro-tensile bond strength, degree of conversion, and antibacterial effectiveness against Staphylococcus Aureus. An investigation using scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2024 Apr;253:112888. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2024.112888. Epub 2024 Mar 7. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2024. PMID: 38471422
-
Antibacterial Properties and Shear Bond Strength of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Incorporated into an Orthodontic Adhesive: A Systematic Review.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024 Jan;17(1):102-108. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2729. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024. PMID: 38559855 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Iron and Magnesium Co-substituted Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles in Orthodontic Composite: A Preliminary Assessment.Cureus. 2024 Mar 18;16(3):e56388. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56388. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38633975 Free PMC article.
-
Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Cerium Nanoparticles Using Spirulina platensis: Assessing Antibacterial and Anti-inflammatory Efficacy.Cureus. 2024 Oct 14;16(10):e71502. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71502. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39544550 Free PMC article.
-
Current applications and future perspectives on rare-earth-based materials in stomatology.iScience. 2025 Jul 26;28(9):113220. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.113220. eCollection 2025 Sep 19. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40822902 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2014. Nanoparticles’ promises and risks: characterization, manipulation, and potential hazards to humanity and the environment.
-
- Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2019. Toxicity of nanomaterials: environmental and healthcare applications.
-
- Nanotechnology in orthodontics. Padmanabhan S. Semin Orthod. 2023;29:79–84.
-
- Biosynthesis, characterization of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Ceratonia siliqua and evaluation of antioxidant and cytotoxicity activities. Javadi F, Yazdi ME, Baghani M, Es-haghi A. Mater Res Express. 2019;6:65408.
-
- Characterization of cerium oxide nanoparticles-part 2: nonsize measurements. Baalousha M, Ju-Nam Y, Cole PA, et al. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2012;31:994–1003. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
