Unraveling Impact of Hemoglobin F and A2 Levels: Correlation With Disease Severity and Treatment Response in Transfusion-Dependent Beta-Thalassemia
- PMID: 38344549
- PMCID: PMC10853895
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.52002
Unraveling Impact of Hemoglobin F and A2 Levels: Correlation With Disease Severity and Treatment Response in Transfusion-Dependent Beta-Thalassemia
Abstract
Background: Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) has been reported to be associated with disease severity and treatment response to HbF-inducing therapies like Hydroxyurea and thalidomide in patients suffering from transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia (TDT). However, the role of hemoglobin A2 (HbA2) remains less clear in TDT, therefore this study aims to determine the impact of both HbF and HbA2 levels on disease severity and treatment response.
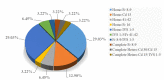
Methodology: A prospective observational study was conducted at the Peshawar Institute of Medical Sciences and Fatimid Foundation Peshawar from May 2023 to October 2023. A total of 232 TDT-diagnosed patients were enrolled using a convenient sampling technique, whereas coinheritance of beta-thalassemia with other hemoglobinopathies was excluded.
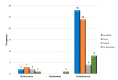
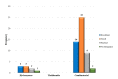
Result: This study reveals a significant impact of HbF on disease severity (p<0.05) but finds no substantial correlation (p>0.05) between HbA2 levels and disease severity. Additionally, HbF and HbA2 levels exhibit no association with treatment response categories in patients receiving HbF induction therapy, and various mutations do not significantly alter HbF and HbA2 levels or disease severity parameters in TDT patients.
Conclusion: The study established a significant association between HbF and disease severity. However, regarding treatment response, neither HbF nor HbA2 levels impact response categories. Combinatorial treatment with hydroxyurea and thalidomide showed superior efficacy compared to monotherapy. A larger sample size and extended follow-up are recommended to further explore the impact of HbF, HbA2, and various mutations on disease severity and treatment response.
Keywords: disease severity parameters; hbf induction response; hemoglobin a2 level; hemoglobin f level; transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia patient.
Copyright © 2024, Nawaz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can Couples With MCV≥80, MCH<26, HbA2<3.2, HbF<3 be Classified as Low-risk β-Thalassemia Group?J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019 May;41(4):303-306. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000001423. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30676434
-
Measurement of HbA₂ by capillary electrophoresis for diagnosing β-thalassemia/HbE disease in patients with low HbF.Lab Med. 2014 Summer;45(3):226-30. doi: 10.1309/LMGD96HES3DZRBZM. Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 25051074
-
Reference intervals for HbA2 and HbF and cut-off value of HbA2 for β-thalassemia carrier screening in a Guizhou population of reproductive age.Clin Biochem. 2019 Mar;65:24-28. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.11.007. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Clin Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30503531
-
Using Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats gene editing to induce permanent expression of fetal hemoglobin in β-thalassemia and sickle cell disease: A comparative meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 29;9:943631. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.943631. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36250099 Free PMC article.
-
[Reaserch Advances on Induction of Fetal Hemoglobin (HbF) by Drugs in the Treatment of β-Thalassemia--Review].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Aug;28(4):1424-1428. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2020.04.059. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32798438 Review. Chinese.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
