Prevalence and immunopathologic characteristics of seropositive and seronegative hepatitis B virus-associated membranous nephropathy: a retrospective study of 420 biopsy-proven cases
- PMID: 38345079
- PMCID: PMC10863513
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2313180
Prevalence and immunopathologic characteristics of seropositive and seronegative hepatitis B virus-associated membranous nephropathy: a retrospective study of 420 biopsy-proven cases
Abstract
Background: This retrospective study aims to investigate the prevalence and immunopathologic characteristics of seropositive and seronegative hepatitis B virus-associated membranous nephropathy (HBV-MN).
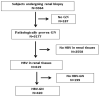
Methods: Clinicopathologic and serologic records of 420 patients with histologically confirmed HBV-MN between January 2014 and July 2021 were examined to determine the prevalence of seropositive and seronegative HBV-MN. Serum anti-PLA2R antibody testing was conducted on 280 patients with HBV-associated membranous nephropathy (HBV-MN) from August 2018 to July 2021. Immunopathologic characteristics of HBV-MN patients and anti-PLA2R antibody positivity were analyzed.
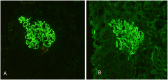
Results: Among 420 pathologically confirmed HBV-MN patients, 230 (54.8%) were seropositive for HBV. The seropositive group exhibited higher blood creatinine values and incidence of liver function abnormalities than the seronegative group (p < .05). Serum anti-PLA2R antibody testing on 280 HBV-MN patients revealed a total positive rate of 44.6%, with the seronegative group showing a significantly higher rate (62.6%) compared to the seropositive group (32.1%) (p < .01). The anti-PLA2R antibody-positive group displayed higher levels of urine protein (p < .05), serum cholesterol (p < .01), and IgG4 subtypes (p < .05) compared to the negative group. Additionally, the positive group had significantly lower levels of serum albumin and IgG than the negative group (p < .01).
Conclusions: This comprehensive study reveals a significantly higher prevalence of seronegative HBV-MN than previously thought. The blood creatinine values and incidence of liver function abnormalities was higher in the serology-positive group than in the serology-negative group. Notably, the seronegative group displayed a higher positive rate of anti-PLA2R antibodies compared to the seropositive group, indicating distinctive clinical and immunopathologic features.
Keywords: HBV-associated membranous nephropathy (HBV-MN); Hepatitis B virus; anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody; membranous nephropathy (MN); seroprevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of hepatitis B associated membranous nephropathy and idiopathic membranous nephropathy complicated with hepatitis B virus infection.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 15;11(1):18407. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98010-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34526634 Free PMC article.
-
[Role of M-type phospholipase A2 receptor and its antibody in hepatitis B virus-associated membranous nephropathy].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Oct 28;41(10):1064-1068. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2016.10.009. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 27807329 Chinese.
-
Favorable outcome in PLA2R positive HBV-associated membranous nephropathy.BMC Nephrol. 2022 Jul 11;23(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02871-y. BMC Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35818032 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical usefulness of autoantibodies to M-type phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) for monitoring disease activity in idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN).Autoimmun Rev. 2016 Feb;15(2):146-54. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.10.004. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2016. PMID: 26527329 Review.
-
Sjögren's syndrome complicated with membranous nephropathy, a cause or coincidence?Int J Rheum Dis. 2021 Aug;24(8):1086-1094. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14168. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021. PMID: 34223708 Review.
References
-
- WHO. Global progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections, 2021. Accountability for the global health sector strategies 2016–2021: Actions for impact. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240027077
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
