Transcription activation in Escherichia coli and Salmonella
- PMID: 38345370
- PMCID: PMC11636354
- DOI: 10.1128/ecosalplus.esp-0039-2020
Transcription activation in Escherichia coli and Salmonella
Abstract
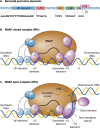
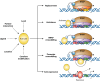
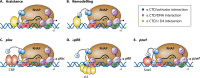
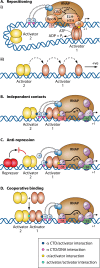
Promoter-specific activation of transcript initiation provides an important regulatory device in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Here, we describe the different mechanisms that operate, focusing on how they have evolved to manage the "housekeeping" bacterial transcription machinery. Some mechanisms involve assisting the bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase or replacing or remodeling one of its subunits. Others are directed to chromosomal DNA, improving promoter function, or relieving repression. We discuss how different activators work together at promoters and how the present complex network of transcription factors evolved.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; RNA polymerase; bacteria; evolution; initiation; promoters; sigma factors; stress adaptation; transcription; transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

