A longitudinal analysis of the impact of nonsurgical and surgical treatment of peri-implantitis upon clinical parameters and implant stability quotient values. A 2-3-year follow-up
- PMID: 38345521
- PMCID: PMC10838112
- DOI: 10.1002/cre2.833
A longitudinal analysis of the impact of nonsurgical and surgical treatment of peri-implantitis upon clinical parameters and implant stability quotient values. A 2-3-year follow-up
Abstract
Objectives: In this study, the aim was to investigate the medium- to long-term impact of peri-implantitis treatment upon clinical parameters and implant stability quotient values and to ascertain if magnetic resonance frequency analysis can be used as a diagnostic tool to demonstrate postoperative healing following treatment of peri-implantitis.
Materials and methods: A total of n = 26 patients (n = 86 implants) diagnosed with peri-implantitis were recruited for this prospective cohort study and four different treatment modalities were used. Baseline measurements of a number of clinical parameters as well as implant stability measurements in the form of ISQ were recorded. These measurements were repeated at 6, 12, and 24-36 months following treatment. Analysis of variance was performed for all implants treated as well as separately for each treatment modality. A regression model was also used to determine factors affecting ISQ measurements over time.
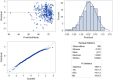
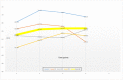
Results: Treatment of peri-implantitis resulted in significant improvements of both average PPDs and BOP (p < .0001 and p < .01). ISQ values marginally improved initially for all treatment modalities, but improvement was only maintained for 2-3 years in treatment modalities I (+1.28), III (+1.49), and IV (+2.92). There was a statistically significant negative linear correlation between average PPD and the ISQ values recorded both at baseline (r = -.618, p < 0.0001) and at 2/3 years (r = -.604, p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Over the 2-3-year follow-up period, all four treatment modalities led to improved clinical and radiographic peri-implant parameters but implant stability posttreatment, as indicated by the fact that the recorded ISQ scores remained stable. As a result, use of MRFA as an adjunct to the traditionally used periodontal and radiographic tools for the evaluation of postoperative implant stability following the treatment of peri-implant disease cannot be recommended.
Keywords: L-PRF; dental implants; peri-implantitis; surgical treatment.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof Renvert receives research grants and fees from Geistlich Pharma outside the present work. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic accuracy of the implant stability quotient in monitoring progressive peri-implant bone loss: An experimental study in dogs.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018 Oct;29(10):1016-1024. doi: 10.1111/clr.13368. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018. PMID: 30267449
-
Comparison of peri-implant crevicular fluid levels of adrenomedullin and human beta defensins 1 and 2 from mandibular implants with different implant stability quotient levels in nonsmoker patients.J Periodontal Res. 2014 Aug;49(4):480-8. doi: 10.1111/jre.12127. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Periodontal Res. 2014. PMID: 23898869
-
Supportive peri-implant therapy following anti-infective surgical peri-implantitis treatment: 5-year survival and success.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018 Jan;29(1):1-6. doi: 10.1111/clr.12910. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018. PMID: 27335316
-
Group 4 ITI Consensus Report: Risks and biologic complications associated with implant dentistry.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018 Oct;29 Suppl 16:351-358. doi: 10.1111/clr.13307. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018. PMID: 30328181
-
Treatment modalities for peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis.Am J Dent. 2013 Dec;26(6):313-8. Am J Dent. 2013. PMID: 24640434 Review.
References
-
- Berglundh, T. , Armitage, G. , Araujo, M. G. , Avila‐Ortiz, G. , Blanco, J. , Camargo, P. M. , Chen, S. , Cochran, D. , Derks, J. , Figuero, E. , Hämmerle, C. H. F. , Heitz‐Mayfield, L. J. A. , Huynh‐Ba, G. , Iacono, V. , Koo, K. T. , Lambert, F. , McCauley, L. , Quirynen, M. , Renvert, S. , … Zitzmann, N. (2018). Peri‐implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 world workshop on the classification of periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 45(Suppl 20), S286–S291. 10.1111/jcpe.12957 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Castro, A. B. , Meschi, N. , Temmerman, A. , Pinto, N. , Lambrechts, P. , Teughels, W. , & Quirynen, M. (2017). Regenerative potential of leucocyte‐ and platelet‐rich fibrin. Part A: Intra‐bony defects, furcation defects and periodontal plastic surgery. A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 44(1), 67–82. 10.1111/jcpe.12643 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials