Disease-Associated Neurotoxic Astrocyte Markers in Alzheimer Disease Based on Integrative Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing
- PMID: 38345650
- PMCID: PMC10861702
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-024-01453-w
Disease-Associated Neurotoxic Astrocyte Markers in Alzheimer Disease Based on Integrative Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing
Abstract
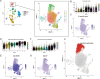
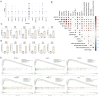
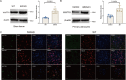
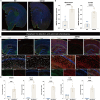
Alzheimer disease (AD) is an irreversible neurodegenerative disease, and astrocytes play a key role in its onset and progression. The aim of this study is to analyze the characteristics of neurotoxic astrocytes and identify novel molecular targets for slowing down the progression of AD. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) data were analyzed from various AD cohorts comprising about 210,654 cells from 53 brain tissue. By integrating snRNA-seq data with bulk RNA-seq data, crucial astrocyte types and genes associated with the prognosis of patients with AD were identified. The expression of neurotoxic astrocyte markers was validated using 5 × FAD and wild-type (WT) mouse models, combined with experiments such as western blot, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), and immunofluorescence. A group of neurotoxic astrocytes closely related to AD pathology was identified, which were involved in inflammatory responses and pathways related to neuron survival. Combining snRNA and bulk tissue data, ZEP36L, AEBP1, WWTR1, PHYHD1, DST and RASL12 were identified as toxic astrocyte markers closely related to disease severity, significantly elevated in brain tissues of 5 × FAD mice and primary astrocytes treated with Aβ. Among them, WWTR1 was significantly increased in astrocytes of 5 × FAD mice, driving astrocyte inflammatory responses, and has been identified as an important marker of neurotoxic astrocytes. snRNA-seq analysis reveals the biological functions of neurotoxic astrocytes. Six genes related to AD pathology were identified and validated, among which WWTR1 may be a novel marker of neurotoxic astrocytes.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; Biomarkers; Bulk RNA-seq; Neurotoxic astrocytes; snRNA-seq.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Andersen JV, Markussen KH, Jakobsen E, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS, Rosenberg PA, Aldana BI (2021) Glutamate metabolism and recycling at the excitatory synapse in health and neurodegeneration. Neuropharmacology 196:108719. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108719 - PubMed
-
- Andl T, Zhou L, Yang K, Kadekaro AL, Zhang Y (2017) YAP and WWTR1: New targets for skin cancer treatment. Cancer Lett 396:30–41. 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.001 - PubMed
-
- Balu DT, Pantazopoulos H, Huang CCY, Muszynski K, Harvey TL, Uno Y, Rorabaugh JM, Galloway CR, Botz-Zapp C, Berretta S, Weinshenker D, Coyle JT (2019) Neurotoxic astrocytes express the d-serine synthesizing enzyme, serine racemase, in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 130:104511. 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104511 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barres BA (2008) The mystery and magic of glia: a perspective on their roles in health and disease. Neuron 60(3):430–440. 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.10.013 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

