Safety and Efficacy of Hybrid Cooperative Complexes of Sodium Hyaluronate and Sodium Chondroitin for the Treatment of Patients with Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 38345716
- PMCID: PMC10920506
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-024-00643-8
Safety and Efficacy of Hybrid Cooperative Complexes of Sodium Hyaluronate and Sodium Chondroitin for the Treatment of Patients with Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) represents a widespread degenerative disease that causes pain and motor disability. Conservative treatments mainly focus on relieving symptoms, improving joint function, and trying to delay surgery. Safety and efficacy of hybrid cooperative complexes (2.4% sodium hyaluronate and 1.6% sodium chondroitin; HA-SC) for symptomatic KOA were investigated in a single-arm, prospective, pilot study.
Methods: Patients with a visual analogue scale (VAS) pain score ≥ 4 and Kellgren-Lawrence Grade < 4 received a single intraarticular HA-SC injection. Patients with a VAS score change from baseline ≤ 1 received a second injection at day 30. Device-related adverse events (DR-AEs)/adverse events (AEs) were primary endpoints. Secondary endpoints included Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index LK 3.1 (WOMAC LK 3.1), VAS, patient global assessment of disease status (PtGA), and patient proportion needing a second injection.
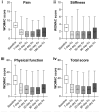
Results: Of 83 patients with KOA (Kellgren-Lawrence Grade, 2-3), 34.9% had DR-AEs at day 7. No serious DR-AEs/AEs were reported. A significant (P < 0.0001) reduction over time in VAS pain score plus WOMAC pain, stiffness, physical function limitation, and total scores was reported. Median PtGA scores indicated a 'slight improvement' at most follow-up visits. Only 18.1% of patients required a second injection.
Conclusions: A single intraarticular HA-SC injection was safe, well-tolerated, and did not lead to major deterioration in terms of reducing knee pain, stiffness, and physical function limitation in patients with symptomatic KOA.
Keywords: Conservative therapy; Hyaluronic acid; Injections; Knee; Osteoarthritis; SINOGEL®; Viscosupplementation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Cristiano Sconza, Dario Romano, Dalila Scaturro, Giulia Letizia Mauro, Giulia Leonardi, Angelo Alito, Stefano Respizzi, Elizaveta Kon, and Berardo Di Matteo declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An Open-Labeled Randomized Prospective Multi-center Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Intra-articular Injection of OSSINEXT™, an Autologous Growth Factor Concentrate (AGFC) Compared to Hyaluronic Acid (HA) in Knee Osteoarthritis.Cureus. 2022 Nov 3;14(11):e31058. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31058. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36475131 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing efficacy of a single intraarticular injection of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) combined with different hyaluronans for knee osteoarthritis: a randomized-controlled clinical trial.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Nov 4;23(1):954. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05906-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 36329428 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[The efficacy and safety of intra-articular application of a combination of sodium hyaluronate and chondroitin sulfate for osteoarthritis of the knee: a multicenter prospective study].Ter Arkh. 2020 Jun 5;92(5):46-54. doi: 10.26442/00403660.2020.05.000631. Ter Arkh. 2020. PMID: 32598775 Russian.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Injecting Mesenchymal Stem Cells Into a Human Knee Joint To Treat Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2022 May 8;14(5):e24823. doi: 10.7759/cureus.24823. eCollection 2022 May. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35693367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects and safety of the combination of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and hyaluronic acid (HA) in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Apr 11;21(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03262-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32278352 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of Adequate Disinfection Techniques for Ultrasound-Guided Injections in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Apr 5;15(7):933. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15070933. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical Mechanisms and Rehabilitation Strategies in Osteoporosis-Related Pain: A Systematic Review.Clin Pract. 2024 Dec 19;14(6):2737-2758. doi: 10.3390/clinpract14060216. Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 39727804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential of Intra-Articular Therapies in Managing Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review.Clin Pract. 2024 Sep 25;14(5):1970-1996. doi: 10.3390/clinpract14050157. Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 39451872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porcine-Derived Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium Alleviates Osteoarthritis in HTB-94 Cells and MIA-Induced SD Rat Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 9;26(2):521. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020521. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859238 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

