Determination of elevated eosinophil to lymphocyte ratio, eosinophil to neutrophil ratio, eosinophil to monocyte ratio and its association with severe vitiligo: A retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38346060
- PMCID: PMC10861031
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296626
Determination of elevated eosinophil to lymphocyte ratio, eosinophil to neutrophil ratio, eosinophil to monocyte ratio and its association with severe vitiligo: A retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Hematological markers such as eosinophil-to-lymphocyte (ELR), eosinophil-to-neutrophil (ENR), and eosinophil-to-monocyte (EMR) ratios may be used in the assessment of skin diseases. However, the relationship with vitiligo remains unclear.
Objectives: We investigated ELR, ENR, and EMR in vitiligo patients and the association with severe vitiligo.
Methods: This study included patients of all ages diagnosed with vitiligo between 2005-2020. ELR, EMR, and ENR were calculated from complete blood counts within 30 days of the first recorded vitiligo diagnosis and 12-18 months before the vitiligo diagnosis. We evaluated the associations between ELR, ENR, and EMR and vitiligo.
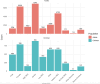
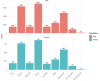
Results: 9,826 vitiligo patients (8,398 adults and 1,428 children) and 8,951 age and sex-matched controls were included in this study. We found that ELR, EMR, and ENR were higher in children than in adults. Patients with vitiligo had higher ENR and EMR than their matched controls. Patients with severe vitiligo had higher ELR, ENR, and EMR compared to patients with mild vitiligo. Patients with increased ENR and EMR 12-18 months before the vitiligo diagnosis had a higher chance of having severe vitiligo (ENR: OR = 7.40, p<0.001, EMR: OR = 3.17, p<0.001).
Conclusion: ELR, ENR, and EMR may be used in the assessment and prognosis of vitiligo, especially in severe cases.
Copyright: © 2024 Weissmann et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of hematological ratios with psoriasis: a nationwide retrospective cohort study.Int J Dermatol. 2024 Oct;63(10):1369-1374. doi: 10.1111/ijd.17133. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Int J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38459652
-
Association of severity of allergic rhinitis with neutrophil-to-lymphocyte, eosinophil-to-neutrophil, and eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratios in adults.Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021 Sep 1;49(5):94-99. doi: 10.15586/aei.v49i5.204. eCollection 2021. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021. PMID: 34476928
-
Hematological Markers in Children and Adults with Atopic Dermatitis: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Dermatology. 2024;240(4):597-605. doi: 10.1159/000539365. Epub 2024 May 28. Dermatology. 2024. PMID: 38797158
-
Association of haemato-biochemical indices and blood composite ratios with microfilaridermia in Onchocerciasis patients.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Apr 8;24(1):384. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09278-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38589790 Free PMC article.
-
Novel index, neutrophil percentage (%) is a useful marker for disease activity in MOG antibody-associated disease.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023 Aug;76:104796. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2023.104796. Epub 2023 Jun 10. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023. PMID: 37320937 Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated hematologic ratios are correlated with acne severity: a national, retrospective cohort study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 31;11:1475117. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1475117. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39544384 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics of adrenal crisis in 371 adult patients with glucocorticoid-induced adrenal insufficiency.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 17;15:1510433. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1510433. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39741879 Free PMC article.
-
Hematological ratios as an indicator of severity in alopecia areata: A retrospective nationwide study.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 2;19(12):e0314600. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314600. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39621703 Free PMC article.
-
Association of eosinophil-to-monocyte ratio with asthma exacerbations in adults: a cross-sectional analysis of NHANES data.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Apr 11;25(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03617-w. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40217197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alikhan A, Felsten LM, Daly M, Petronic-Rosic V. Vitiligo: a comprehensive overview Part I. Introduction, epidemiology, quality of life, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, associations, histopathology, etiology, and work-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011. Sep;65(3):473–491. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.11.061 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Awad SS, Tadros E. Understanding the Role of Lymphocytes in Vitiligo. Int J Immunol Immunother 8:060. 2021. doi: 10.23937/2378-3672/1410060 - DOI
-
- Alan S, Tuna S, Türkoğlu EB. The relation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and mean platelet volume with the presence and severity of Behçet’s syndrome. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2015. Dec;31(12):626–31. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2015.10.010 Epub 2015 Dec 10. . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical