Histotripsy: A Method for Mechanical Tissue Ablation with Ultrasound
- PMID: 38346277
- PMCID: PMC11837764
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-073123-022334
Histotripsy: A Method for Mechanical Tissue Ablation with Ultrasound
Abstract
Histotripsy is a relatively new therapeutic ultrasound technology to mechanically liquefy tissue into subcellular debris using high-amplitude focused ultrasound pulses. In contrast to conventional high-intensity focused ultrasound thermal therapy, histotripsy has specific clinical advantages: the capacity for real-time monitoring using ultrasound imaging, diminished heat sink effects resulting in lesions with sharp margins, effective removal of the treated tissue, a tissue-selective feature to preserve crucial structures, and immunostimulation. The technology is being evaluated in small and large animal models for treating cancer, thrombosis, hematomas, abscesses, and biofilms; enhancing tumor-specific immune response; and neurological applications. Histotripsy has been recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat liver tumors, with clinical trials undertaken for benign prostatic hyperplasia and renal tumors. This review outlines the physical principles of various types of histotripsy; presents major parameters of the technology and corresponding hardware and software, imaging methods, and bioeffects; and discusses the most promising preclinical and clinical applications.
Keywords: HIFU; boiling; cavitation; focused ultrasound surgery; high-intensity focused ultrasound; histotripsy; mechanical bioeffects; nonlinear waves.
Figures
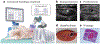

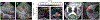
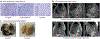
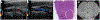

References
-
- Li F, Chen J, Yin L, Zeng D, Wang L, et al. 2023. HIFU as an alternative modality for patients with uterine fibroids who require fertility-sparing treatment. Int. J. Hyperth 40:2155077 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 CA211217/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA258581/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB008998/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141967/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB034399/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091267/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB037129/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001619/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R21 NS093121/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS108042/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA260684/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB028309/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB032772/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

