Understanding metric-related pitfalls in image analysis validation
- PMID: 38347140
- PMCID: PMC11181963
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-023-02150-0
Understanding metric-related pitfalls in image analysis validation
Abstract
Validation metrics are key for tracking scientific progress and bridging the current chasm between artificial intelligence research and its translation into practice. However, increasing evidence shows that, particularly in image analysis, metrics are often chosen inadequately. Although taking into account the individual strengths, weaknesses and limitations of validation metrics is a critical prerequisite to making educated choices, the relevant knowledge is currently scattered and poorly accessible to individual researchers. Based on a multistage Delphi process conducted by a multidisciplinary expert consortium as well as extensive community feedback, the present work provides a reliable and comprehensive common point of access to information on pitfalls related to validation metrics in image analysis. Although focused on biomedical image analysis, the addressed pitfalls generalize across application domains and are categorized according to a newly created, domain-agnostic taxonomy. The work serves to enhance global comprehension of a key topic in image analysis validation.
© 2024. Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: F.B. is an employee of Siemens AG (Munich, Germany). B.v.G. is a shareholder of Thirona (Nijmegen, NL). B.G. is an employee of HeartFlow Inc (California, USA) and Kheiron Medical Technologies Ltd (London, UK). M.M.H. received an Nvidia GPU Grant. Th. K. is an employee of Lunit (Seoul, South Korea). G.L. is on the advisory board of Canon Healthcare IT (Minnetonka, USA) and is a shareholder of Aiosyn BV (Nijmegen, NL). Na.R. is the founder and CSO of Histofy (New York, USA). Ni.R. is an employee of Nvidia GmbH (Munich, Germany). J.S.-R. reports funding from GSK (Heidelberg, Germany), Pfizer (New York, USA) and Sanofi (Paris, France) and fees from Travere Therapeutics (California, USA), Stadapharm (Bad Vilbel, Germany), Astex Therapeutics (Cambridge, UK), Pfizer (New York, USA), and Grunenthal (Aachen, Germany). R.M.S. receives patent royalties from iCAD (New Hampshire, USA), ScanMed (Nebraska, USA), Philips (Amsterdam, NL), Translation Holdings (Alabama, USA) and PingAn (Shenzhen, China); his lab received research support from PingAn through a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement. S.A.T. receives financial support from Canon Medical Research Europe (Edinburgh, Scotland). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


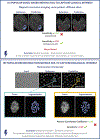
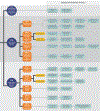
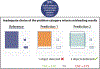



Update of
-
Understanding metric-related pitfalls in image analysis validation.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 23:arXiv:2302.01790v4. ArXiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Methods. 2024 Feb;21(2):182-194. doi: 10.1038/s41592-023-02150-0. PMID: 36945687 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Brown Bernice B. Delphi process: a methodology used for the elicitation of opinions of experts. Technical report, Rand Corp Santa Monica CA, 1968.
-
- Carbonell Alberto, De la Pena Marcos, Flores Ricardo, and Gago Selma. Effects of the trinucleotide preceding the self-cleavage site on eggplant latent viroid hammerheads: differences in co-and post-transcriptional self-cleavage may explain the lack of trinucleotide auc in most natural hammerheads. Nucleic acids research, 34(19):5613–5622, 2006. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Jianxu, Ding Liya, Viana Matheus P, Lee HyeonWoo, Sluezwski M Filip, Morris Benjamin, Hendershott Melissa C, Yang Ruian, Mueller Irina A, and Rafelski Susanne M. The allen cell and structure segmenter: a new open source toolkit for segmenting 3d intracellular structures in fluorescence microscopy images. BioRxiv, page 491035, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

