Metrics reloaded: recommendations for image analysis validation
- PMID: 38347141
- PMCID: PMC11182665
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-023-02151-z
Metrics reloaded: recommendations for image analysis validation
Abstract
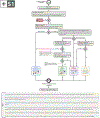
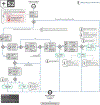
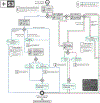
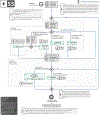
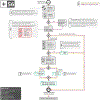
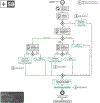
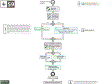
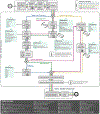
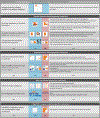
Increasing evidence shows that flaws in machine learning (ML) algorithm validation are an underestimated global problem. In biomedical image analysis, chosen performance metrics often do not reflect the domain interest, and thus fail to adequately measure scientific progress and hinder translation of ML techniques into practice. To overcome this, we created Metrics Reloaded, a comprehensive framework guiding researchers in the problem-aware selection of metrics. Developed by a large international consortium in a multistage Delphi process, it is based on the novel concept of a problem fingerprint-a structured representation of the given problem that captures all aspects that are relevant for metric selection, from the domain interest to the properties of the target structure(s), dataset and algorithm output. On the basis of the problem fingerprint, users are guided through the process of choosing and applying appropriate validation metrics while being made aware of potential pitfalls. Metrics Reloaded targets image analysis problems that can be interpreted as classification tasks at image, object or pixel level, namely image-level classification, object detection, semantic segmentation and instance segmentation tasks. To improve the user experience, we implemented the framework in the Metrics Reloaded online tool. Following the convergence of ML methodology across application domains, Metrics Reloaded fosters the convergence of validation methodology. Its applicability is demonstrated for various biomedical use cases.
© 2024. Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare the following competing interests: Under his terms of employment, M.B.B. is entitled to stock options in Mona.health, a KU Leuven spinoff. F.B. is an employee of Siemens AG (Munich, Germany). F.B. reports funding from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). B.v.G. is a shareholder of Thirona (Nijmegen, NL). B.G. was an employee of HeartFlow Inc (California, USA) and Kheiron Medical Technologies Ltd (London, UK). M.M.H. received an Nvidia GPU Grant. B.K. is a consultant for ThinkSono Ldt (London, UK). G.L. is on the advisory board of Canon Healthcare IT (Minnetonka, USA) and is a shareholder of Aiosyn BV (Nijmegen, NL). N.R. is an employee of Nvidia GmbH (Munich, Germany). J.S.-R. reports funding from GSK (Heidelberg, Germany), Pfizer (New York, USA) and Sanofi (Paris, France) and fees from Travere Therapeutics (California, USA), Stadapharm (Bad Vilbel, Germany), Astex Therapeutics (Cambridge, UK), Pfizer (New York, USA), and Grunenthal (Aachen, Germany). R.M.S. receives patent royalties from iCAD (New Hampshire, USA), ScanMed (Nebraska, USA), Philips (Amsterdam, NL), Translation Holdings (Alabama, USA) and PingAn (Shenzhen, China); his lab received research support from PingAn through a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement. S.A.T. receives financial support from Canon Medical Research Europe (Edinburgh, Scotland). The remaining authors declare no competing interests
Figures




References
-
- Adamson Adewole S and Smith Avery. Machine learning and health care disparities in dermatology, 2018. - PubMed
-
- Armato Samuel G III, McLennan Geoffrey, Bidaut Luc, McNitt-Gray Michael F, Meyer Charles R, Reeves Anthony P, Zhao Binsheng, Aberle Denise R, Henschke Claudia I, Hoffman Eric A, et al. The lung image database consortium (lidc) and image database resource initiative (idri): a completed reference database of lung nodules on ct scans. Medical physics, 38(2):915–931, 2011. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birhane Abeba, Kalluri Pratyusha, Card Dallas, Agnew William, Dotan Ravit, and Bao Michelle. The values encoded in machine learning research. arXiv, June 2021.

