Screening ovarian cancer by using risk factors: machine learning assists
- PMID: 38347611
- PMCID: PMC10863117
- DOI: 10.1186/s12938-024-01219-x
Screening ovarian cancer by using risk factors: machine learning assists
Abstract
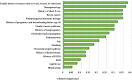
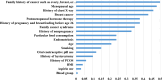
Background and aim: Ovarian cancer (OC) is a prevalent and aggressive malignancy that poses a significant public health challenge. The lack of preventive strategies for OC increases morbidity, mortality, and other negative consequences. Screening OC through risk prediction could be leveraged as a powerful strategy for preventive purposes that have not received much attention. So, this study aimed to leverage machine learning approaches as predictive assistance solutions to screen high-risk groups of OC and achieve practical preventive purposes.
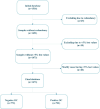
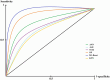
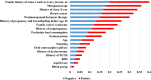
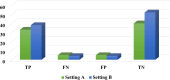
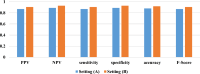
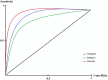
Materials and methods: As this study is data-driven and retrospective in nature, we leveraged 1516 suspicious OC women data from one concentrated database belonging to six clinical settings in Sari City from 2015 to 2019. Six machine learning (ML) algorithms, including XG-Boost, Random Forest (RF), J-48, support vector machine (SVM), K-nearest neighbor (KNN), and artificial neural network (ANN) were leveraged to construct prediction models for OC. To choose the best model for predicting OC, we compared various prediction models built using the area under the receiver characteristic operator curve (AU-ROC).
Results: Current experimental results revealed that the XG-Boost with AU-ROC = 0.93 (0.95 CI = [0.91-0.95]) was recognized as the best-performing model for predicting OC.
Conclusions: ML approaches possess significant predictive efficiency and interoperability to achieve powerful preventive strategies leveraging OC screening high-risk groups.
Keywords: Machine learning; Ovarian cancer; Predictive efficiency; Preventive strategy; Public health challenge.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optimizing prediction of metastasis among colorectal cancer patients using machine learning technology.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 18;25(1):272. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03841-y. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40251500 Free PMC article.
-
Design of risk prediction model for esophageal cancer based on machine learning approach.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 20;10(2):e24797. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24797. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38312629 Free PMC article.
-
A metabolic fingerprint of ovarian cancer: a novel diagnostic strategy employing plasma EV-based metabolomics and machine learning algorithms.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Feb 12;18(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01590-w. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 39940000 Free PMC article.
-
[Construction of a predictive model for in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in intensive care unit based on machine learning].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Jul;35(7):696-701. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20221219-01104. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37545445 Chinese.
-
Identifying Explainable Machine Learning Models and a Novel SFRP2+ Fibroblast Signature as Predictors for Precision Medicine in Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 29;24(23):16942. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316942. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069266 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Explainable AI-based feature importance analysis for ovarian cancer classification with ensemble methods.Front Public Health. 2025 Mar 26;13:1479095. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1479095. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40206169 Free PMC article.
-
Early Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of the Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Feb 7;15(4):406. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15040406. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparing the Effectiveness of Artificial Intelligence Models in Predicting Ovarian Cancer Survival: A Systematic Review.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025 Mar;8(3):e70138. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.70138. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 40103563 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Cytoreductive Surgery Versus Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Followed by Surgery in Patients with Advanced Primary Epithelial Ovarian Cancer in Low Resources Setting: A Randomized Clinical Trial.J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2025 Jun;75(3):199-205. doi: 10.1007/s13224-024-02061-w. Epub 2024 Nov 6. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2025. PMID: 40584804
-
Establishment of prediction model for mortality risk of pancreatic cancer: a retrospective study.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024 Jun 27;24(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12911-024-02590-4. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024. PMID: 38937795 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

