Novel quinazolines bearing 1,3,4-thiadiazole-aryl urea derivative as anticancer agents: design, synthesis, molecular docking, DFT and bioactivity evaluations
- PMID: 38347613
- PMCID: PMC10863284
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-024-01119-0
Novel quinazolines bearing 1,3,4-thiadiazole-aryl urea derivative as anticancer agents: design, synthesis, molecular docking, DFT and bioactivity evaluations
Abstract
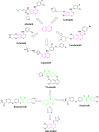
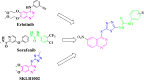
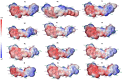
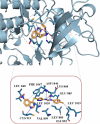
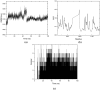
A novel series of 1-(5-((6-nitroquinazoline-4-yl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)-3-phenylurea derivatives 8 were designed and synthesized to evaluate their cytotoxic potencies. The structures of these obtained compounds were thoroughly characterized by IR, 1H, and 13C NMR, MASS spectroscopy and elemental analysis methods. Additionally, their in vitro anticancer activities were investigated using the MTT assay against A549 (human lung cancer), MDA-MB231 (human triple-negative breast cancer), and MCF7 (human hormone-dependent breast cancer). Etoposide was used as a reference marketed drug for comparison. Among the compounds tested, compounds 8b and 8c demonstrated acceptable antiproliferative activity, particularly against MCF7 cells. Considering the potential VEGFR-2 inhibitor potency of these compounds, a molecular docking study was performed for the most potent compound, 8c, to determine its probable interactions. Furthermore, computational investigations, including molecular dynamics, frontier molecular orbital analysis, Fukui reactivity descriptor, electrostatic potential surface, and in silico ADME evaluation for all compounds were performed to illustrate the structure-activity relationship (SAR).
Keywords: Anticancer; In silico ADME; MTT assay; Molecular docking; Quinazoline.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 1,2,4-Thiadiazole-1,2,4-Triazole Derivatives Bearing Amide Functionality as Anticancer Agents.Arab J Sci Eng. 2021;46(1):225-232. doi: 10.1007/s13369-020-04626-z. Epub 2020 May 22. Arab J Sci Eng. 2021. PMID: 32837812 Free PMC article.
-
6-Bromo quinazoline derivatives as cytotoxic agents: design, synthesis, molecular docking and MD simulation.BMC Chem. 2024 Jul 4;18(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01230-2. BMC Chem. 2024. PMID: 38965630 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Thioether-Bridged 2,6-Disubstituted and 2,5,6-Trisubstituted Imidazothiadiazole Analogues: Synthesis, Antiproliferative Activity, ADME, and Molecular Docking Studies.Chem Biodivers. 2023 Jan;20(1):e202200884. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202200884. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Chem Biodivers. 2023. PMID: 36445849
-
Chemical Characterization, In-silico Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Analysis of Antiproliferative Compounds Isolated from the Bark of Anthocephalus cadamba Miq.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(20):3416-3437. doi: 10.2174/1871520622666220204123348. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35125087
-
Novel 1,3-diaryl pyrazole derivatives bearing methylsulfonyl moiety: Design, synthesis, molecular docking and dynamics, with dual activities as anti-inflammatory and anticancer agents through selectively targeting COX-2.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Dec;129:106143. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106143. Epub 2022 Sep 11. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 36191430
Cited by
-
The Structure-Antiproliferative Activity Relationship of Pyridine Derivatives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 11;25(14):7640. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147640. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New 6-nitro-4-substituted quinazoline derivatives targeting epidermal growth factor receptor: design, synthesis and in vitro anticancer studies.Future Med Chem. 2024;16(19):2025-2041. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2024.2389772. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Future Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39230501
References
-
- Guruswamy DKM, et al. Novel 3-(3, 5-difluoro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(naphthalen-2-yl) prop-2-en-1-one as a potent inhibitor of MAP-kinase in HeLa cell lines and anti-angiogenic activity is ediated by HIF-1α in EAC animal model. Oncotarget. 2020;11(50):4661. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27836. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
