Primary vaginal cancer after hysterectomy for benign conditions: a systematic review of the literature
- PMID: 38347832
- PMCID: PMC10859505
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1334778
Primary vaginal cancer after hysterectomy for benign conditions: a systematic review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Primary vaginal cancer is a rare condition. Some studies have revealed an increased risk of vaginal cancer among patients who have undergone hysterectomy for premalignant and malignant cervical disease. However, there is limited literature available on primary vaginal cancer following hysterectomy for benign conditions.
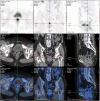
Objectives: This review aimed to investigate available evidence on clinical characteristics, treatments, and outcomes of primary vaginal cancer following hysterectomy for benign diseases. Additionally, we provide a case of a patient who developed primary vaginal cancer 10 years after undergoing hysterectomy for abnormal uterine bleeding.
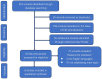
Search strategy: We conducted a comprehensive literature search on PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science using a combination of title and abstract represented by "hysterectomy", and "vaginal cancer"; "vaginal neoplasm"; and "cancer of vagina". No article type restrictions were applied.
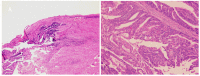
Main results: Eight studies with a total of 56 cases were included in this review. The main symptom observed was vaginal bleeding. Squamous cancer was found to be the most common type, followed by adenocarcinoma. The majority of vaginal cancer cases occurred approximately 10 years after undergoing hysterectomy. The most common location of the tumor was in the vaginal apex. The management approaches varied and details were available in 25 cases. Among these, 7 cases were treated with radiotherapy alone, 1 case received concurrent chemoradiation therapy, and the of rest of the cases underwent surgery as the primary treatment, with or without additional adjuvant therapy. Data of follow-up was available for 15 cases, with 2 cases resulting in death and 2 cases experiencing recurrence. The other cases were alive and well at the time of considered follow up.
Conclusion: Primary vaginal cancer after hysterectomy for benign conditions is an extremely rare condition. It is essential to have high-level evidence to guide the screening and treatment strategy for this rare condition. A part of women who have undergone hysterectomy for benign disorders can benefit from vaginal cytology evaluation. It is reasonable to postpone the initial screening after surgery and to extend the interval between subsequent screenings. Further retrospective case-control trials are expected to determine which specific subgroups of patients mentioned above might most potentially benefit from screening. The treatment decision for vaginal cancer after hysterectomy is more favorable to radiotherapy-based management rather than surgery. Vaginal endometrioid adenocarcinoma may arise from the malignant transformation of endometriosis. More studies are expected to investigate the correlation between these two diseases.
Keywords: endometrioid adenocarcinoma; hysterectomy; systematic review; vaginal cancer; vaginal carcinoma.
Copyright © 2024 Qian, Gracious, Chen and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
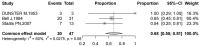
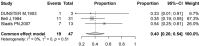
Similar articles
-
Prophylactic Oophorectomy: Reducing the U.S. Death Rate from Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. A Continuing Debate.Oncologist. 1996;1(5):326-330. Oncologist. 1996. PMID: 10388011
-
Levonorgestrel intrauterine system for endometrial protection in women with breast cancer on adjuvant tamoxifen.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 21;12(12):CD007245. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007245.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33348436 Free PMC article.
-
Isthmic-vaginal smear cytology in the follow-up after radical vaginal trachelectomy for early stage cervical cancer: is it safe?Cancer Cytopathol. 2014 May;122(5):349-58. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21402. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014. PMID: 24478265
-
Effectiveness of vaginal Papanicolaou smear screening after total hysterectomy for benign disease.JAMA. 1996 Mar 27;275(12):940-7. JAMA. 1996. PMID: 8598623 Review.
-
Clinical presentation, treatment, and outcomes associated with vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia: A retrospective study of 118 patients.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021 May;47(5):1624-1630. doi: 10.1111/jog.14733. Epub 2021 Mar 23. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021. PMID: 33754436 Review.
Cited by
-
Primary serous borderline tumor arising from the vaginal stump.Gynecol Oncol Rep. 2025 Apr 26;59:101755. doi: 10.1016/j.gore.2025.101755. eCollection 2025 Jun. Gynecol Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40611980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaltenecker B, Dunton CJ, Tikaria R. Vaginal Cancer. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; (2023). Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559126/ - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

