Robotic stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial meningiomas in elderly patients: assessment of treatment efficacy and safety
- PMID: 38347835
- PMCID: PMC10860398
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1329696
Robotic stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial meningiomas in elderly patients: assessment of treatment efficacy and safety
Abstract
Purpose: Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has been increasingly used to treat intracranial pathologies in elderly patients. The treatment efficiency of SRS has been demonstrated in meningiomas, with excellent local control. We aimed to analyze the safety of robotic SRS in elderly patients with meningiomas.
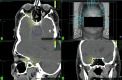
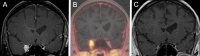
Methods: We searched for patients with suspected WHO °I meningioma ≥ 60 years old, who underwent CyberKnife (CK) SRS from January 2011 to December 2021. Tumor localization was categorized using the "CLASS" algorithmic scale. Tumor response was evaluated using the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria for meningiomas. Adverse effects were graded using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0 and a cox regression was performed to investigate possible predictors.
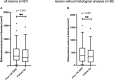
Results: We identified 82 patients with 102 CK-treated lesions that matched the criteria for the first SRS. The median age was 70 [IQR 64-75] years, and 24.3% of the patients were aged > 75 years. Multiple lesions (up to six) were treated in 14.1% of the SRS-sessions. A previous surgery was performed in 57.3% of lesions, with a median time interval of 41 [IQR 10 - 58] months between the initial surgical procedure and the SRS treatment. In 47.9% of cases, CLASS 3 meningiomas at high-risk locations were irradiated. Single fraction radiosurgery was applied to 62.5% of the lesions, while in the remaining cases multi-session SRS with three to five fractions was used. During the median follow-up period of 15.9 months, lesion size progression was observed in 3 cases. Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) declined by ≥ 20 points in four patients. Adverse effects occurred in 13 patients, while only four patients had CTCAE ≥2 toxicities. Hereby only one of these toxicities was persistent. The occurrence of complications was independent of age, planned target volume (PTV), high-risk localization, and surgery before SRS.
Conclusion: The data indicates that SRS is a safe, efficient, and convenient treatment modality for elderly patients with meningioma, even at high-risk locations.
Keywords: CyberKnife; brain tumor; elderly patients; meningioma; stereotactic radiosurgery.
Copyright © 2024 Früh, Bodnar, Nachbar, Gradhand, Kalinauskaite, Rubarth, Truckenmueller, Kaul, Zips, Vajkoczy, Senger and Acker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of CyberKnife radiosurgery in elderly patients with brain metastases: a retrospective clinical evaluation.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Sep 29;15(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01655-8. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32993672 Free PMC article.
-
Image-Guided Robotic Radiosurgery for Treatment of Recurrent Grade II and III Meningiomas. A Single-Center Study.World Neurosurg. 2019 Nov;131:e96-e107. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.07.058. Epub 2019 Jul 12. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31306844
-
The Role of Stereotactic Radiosurgery in the Management of Foramen Magnum Meningiomas-A Multicenter Analysis and Review of the Literature.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 11;14(2):341. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020341. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053504 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery versus stereotactic radiotherapy in the management of intracranial meningiomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Focus. 2019 Jun 1;46(6):E2. doi: 10.3171/2019.3.FOCUS1970. Neurosurg Focus. 2019. PMID: 31153149
-
Outcomes following stereotactic radiosurgery for foramen magnum meningiomas: a single-center experience and systematic review of the literature.Neurosurg Focus. 2022 Nov;53(5):E6. doi: 10.3171/2022.8.FOCUS22299. Neurosurg Focus. 2022. PMID: 36321282
Cited by
-
The safety and efficacy of robotic radiosurgery and radiotherapy in the management of skull base tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Jan 10;48(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03177-x. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 39792270
References
-
- Gittleman HR, Ostrom QT, Rouse CD, Dowling JA, Blank De PM, Kruchko CA, et al. . Trends in central nervous system tumor incidence relative to other common cancers in adults, adolescents, and children in the United States, 2000 to 2010. Cancer. (2015) 121(1):102–12. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

