Oxidative stress and ion channels in neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 38348223
- PMCID: PMC10859863
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1320086
Oxidative stress and ion channels in neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
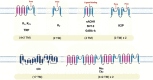
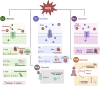
Numerous neurodegenerative diseases result from altered ion channel function and mutations. The intracellular redox status can significantly alter the gating characteristics of ion channels. Abundant neurodegenerative diseases associated with oxidative stress have been documented, including Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, spinocerebellar ataxia, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Huntington's disease. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species compounds trigger posttranslational alterations that target specific sites within the subunits responsible for channel assembly. These alterations include the adjustment of cysteine residues through redox reactions induced by reactive oxygen species (ROS), nitration, and S-nitrosylation assisted by nitric oxide of tyrosine residues through peroxynitrite. Several ion channels have been directly investigated for their functional responses to oxidizing agents and oxidative stress. This review primarily explores the relationship and potential links between oxidative stress and ion channels in neurodegenerative conditions, such as cerebellar ataxias and Parkinson's disease. The potential correlation between oxidative stress and ion channels could hold promise for developing innovative therapies for common neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: antioxidants; calcium channel; glutathione; neurodegenerative disorders; oxidative stress; potassium channels; reactive oxygen species; sodium channels.
Copyright © 2024 Orfali, Alwatban, Orfali, Lau, Chea, Alotaibi, Nam and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
Author RSO is a member of BrainExperiments.com. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adelman J. P., Clapham D. E., Hibino H., Inanobe A., Jan L. Y., Karschin A., et al. (2023). Inwardly rectifying potassium channels (KIR) in GtoPdb v.2023.1. IUPHARBPS Guide Pharmacol. CITE 2023. 10.2218/gtopdb/F74/2023.1 - DOI
-
- Akbarali H. (2014). Oxidative stress and ion channels. Syst. Biol. Free Radic. Antioxid., 355–373. 10.1007/978-3-642-30018-9_12 - DOI

