Application of next-generation sequencing to identify different pathogens
- PMID: 38348304
- PMCID: PMC10859930
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1329330
Application of next-generation sequencing to identify different pathogens
Abstract
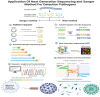
Early and precise detection and identification of various pathogens are essential for epidemiological monitoring, disease management, and reducing the prevalence of clinical infectious diseases. Traditional pathogen detection techniques, which include mass spectrometry, biochemical tests, molecular testing, and culture-based methods, are limited in application and are time-consuming. Next generation sequencing (NGS) has emerged as an essential technology for identifying pathogens. NGS is a cutting-edge sequencing method with high throughput that can create massive volumes of sequences with a broad application prospects in the field of pathogen identification and diagnosis. In this review, we introduce NGS technology in detail, summarizes the application of NGS in that identification of different pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, and analyze the challenges and outlook for using NGS to identify clinical pathogens. Thus, this work provides a theoretical basis for NGS studies and provides evidence to support the application of NGS in distinguishing various clinical pathogens.
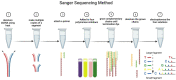
Keywords: Sanger; bacteria; fungi; next generation sequencing; pathogens.
Copyright © 2024 Nafea, Wang, Wang, Salama, Aziz, Xu and Tong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

