Evidence for the gut-skin axis: Common genetic structures in inflammatory bowel disease and psoriasis
- PMID: 38348734
- PMCID: PMC10862160
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13611
Evidence for the gut-skin axis: Common genetic structures in inflammatory bowel disease and psoriasis
Abstract
Background: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and psoriasis (Ps) are common immune-mediated diseases that exhibit clinical comorbidity, possibly due to a common genetic structure. However, the exact mechanism remains unknown.
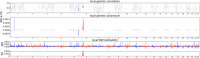
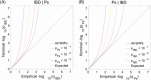
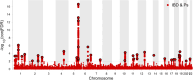
Methods: The study population consisted of IBD and Ps genome-wide association study (GWAS) data. Genetic correlations were first evaluated. Then, the overall evaluation employed LD score regression (LDSC), while the local assessment utilized heritability estimation from summary statistics (HESS). Causality assessment was conducted through two-sample Mendelian randomization (2SMR), and genetic overlap analysis utilized the conditional false discovery rate/conjunctional FDR (cond/conjFDR) method. Finally, LDSC applied to specifically expressed genes (LDSC-SEG) was performed at the tissue level. For IBD and Ps-specific expressed genes, genetic correlation, causality, shared genetics, and trait-specific associated tissues were methodically examined.
Results: At the genomic level, both overall and local genetic correlations were found between IBD and Ps. MR analysis indicated a positive causal relationship between Ps and IBD. The conjFDR analysis with a threshold of < 0.01 identified 43 loci shared between IBD and Ps. Subsequent investigations into disease-associated tissues indicated a close association of IBD and Ps with whole blood, lung, spleen, and EBV-transformed lymphocytes.
Conclusion: The current research offers a novel perspective on the association between IBD and Ps. It contributes to an enhanced comprehension of the genetic structure and mechanisms of comorbidities in both diseases.
Keywords: GWAS; genetic risk loci; genetic structure; gut-skin axis; psoriasis.
© 2024 The Authors. Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construe as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

