Deoxygenative Coupling of CO with a Tetrametallic Magnesium Hydride Complex
- PMID: 38348749
- PMCID: PMC11497278
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202319626
Deoxygenative Coupling of CO with a Tetrametallic Magnesium Hydride Complex
Abstract
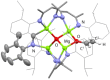
Addition of CO to a tetrametallic magnesium hydride cluster results in both carbon-carbon bond formation and deoxygenation to generate an acetaldehyde enolate [C2OH3]- which remains coordinated to the cluster. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first example of formation of an isolable complex containing an [C2OH3]- fragment from reaction of CO with a metal hydride, and the first example of CO homologation and deoxygenation at a main group metal. DFT studies suggest that key steps in the mechanism involve nucleophilic attack of an oxymethylene on a formyl ligand to generate an unstable [C2O2H3]3- fragment, which undergoes subsequent deoxygenation.
Keywords: Carbon Monoxide; Deoxygenation; Homologation; Hydride; Magnesium.
© 2024 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



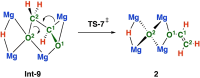
References
-
- West N. M., Miller A. J., Labinger J. A., Bercaw J. E., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 881–898.
-
- Labinger J. A., J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 847, 4–12.
-
- Kong R. Y., Crimmin M. R., Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 16587–16597. - PubMed
-
- Shima T., Hou Z., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8124–8125. - PubMed
-
- Cheng J., Ferguson M. J., Takats J., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2–3. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

