Sensitizing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to cefuroxime: the synergic effect of bicarbonate and the wall teichoic acid inhibitor ticlopidine
- PMID: 38349162
- PMCID: PMC10916381
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.01627-23
Sensitizing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to cefuroxime: the synergic effect of bicarbonate and the wall teichoic acid inhibitor ticlopidine
Abstract
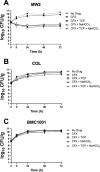
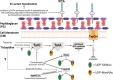
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains are a major challenge for clinicians due, in part, to their resistance to most β-lactams, the first-line treatment for methicillin-susceptible S. aureus. A phenotype termed "NaHCO3-responsiveness" has been identified, wherein many clinical MRSA isolates are rendered susceptible to standard-of-care β-lactams in the presence of physiologically relevant concentrations of NaHCO3, in vitro and ex vivo; moreover, such "NaHCO3-responsive" isolates can be effectively cleared by β-lactams from target tissues in experimental infective endocarditis (IE). One mechanistic impact of NaHCO3 exposure on NaHCO3-responsive MRSA is to repress WTA synthesis. This NaHCO3 effect mimics the phenotype of tarO-deficient MRSA, including sensitization to the PBP2-targeting β-lactam, cefuroxime (CFX). Herein, we further investigated the impacts of NaHCO3 exposure on CFX susceptibility in the presence and absence of a WTA synthesis inhibitor, ticlopidine (TCP), in a collection of clinical MRSA isolates from skin and soft tissue infections (SSTI) and bloodstream infections (BSI). NaHCO3 and/or TCP enhanced susceptibility to CFX in vitro, by both minimum inhibitor concentration (MIC) and time-kill assays, as well as in an ex vivo simulated endocarditis vegetations (SEV) model, in NaHCO3-responsive MRSA. Furthermore, in experimental IE (presumably in the presence of endogenous NaHCO3), pre-exposure to TCP prior to infection sensitized the NaHCO3-responsive MRSA strain (but not the non-responsive strain) to enhanced clearances by CFX in target tissues. These data support the notion that NaHCO3 is acting similarly to WTA synthesis inhibitors, and that such inhibitors have potential translational applications in the treatment of certain MRSA strains in conjunction with specific β-lactam agents.
Keywords: NaHCO3-responsive; experimental infective endocarditis (IE); methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs); wall teichoic acid (WTA) synthesis; β-lactams.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bicarbonate Within: A Hidden Modulator of Antibiotic Susceptibility.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Jan 16;14(1):96. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010096. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Sodium Bicarbonate on Wall Teichoic Acid Synthesis and β-Lactam Sensitization in NaHCO3-Responsive and Nonresponsive Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0342222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03422-22. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36377886 Free PMC article.
-
Bicarbonate Resensitization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus to β-Lactam Antibiotics.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Jun 24;63(7):e00496-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00496-19. Print 2019 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31010857 Free PMC article.
-
Ability of Bicarbonate Supplementation To Sensitize Selected Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains to β-Lactam Antibiotics in an Ex Vivo Simulated Endocardial Vegetation Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Feb 21;64(3):e02072-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02072-19. Print 2020 Feb 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 31844004 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of β-Lactams in the Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infections.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Jun 23;64(7):e00468-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00468-20. Print 2020 Jun 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32312776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bicarbonate Within: A Hidden Modulator of Antibiotic Susceptibility.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Jan 16;14(1):96. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010096. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
D-Serine Can Modify the Wall Teichoic Acid of MRSA via the dlt Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 25;26(9):4110. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094110. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ersoy SC, Otmishi M, Milan VT, Li L, Pak Y, Mediavilla J, Chen L, Kreiswirth B, Chambers HF, Proctor RA, Xiong YQ, Fowler VG, Bayer AS. 2020. Scope and predictive genetic/phenotypic signatures of bicarbonate (NaHCO3) responsiveness and β-lactam sensitization in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 64:e02445-19. doi:10.1128/AAC.02445-19 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

