Interim Report of the Reactogenicity and Immunogenicity of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 XBB-Containing Vaccines
- PMID: 38349280
- PMCID: PMC11326827
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiae067
Interim Report of the Reactogenicity and Immunogenicity of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 XBB-Containing Vaccines
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Interim Report of the Reactogenicity and Immunogenicity of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 XBB-Containing Vaccines.J Infect Dis. 2024 Jul 25;230(1):e219. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae186. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39052752 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Monovalent Omicron XBB.1.5-containing vaccines were approved for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) 2023-2024 immunizations.
Methods: This ongoing, open-label, phase 2/3 study evaluated messenger RNA (mRNA)-1273.815 monovalent (50-µg Omicron XBB.1.5 spike mRNA) and mRNA-1273.231 bivalent (25-µg each Omicron XBB.1.5 and BA.4/BA.5 spike mRNAs) vaccines, administered as fifth doses to adults who previously received primary series, third doses of an original mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, and fourth doses of an Omicron BA.4/BA.5 bivalent vaccine. Interim safety and immunogenicity 29 days after vaccination are reported.
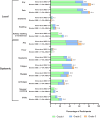
Results: Participants (randomized 1:1) received 50-µg of mRNA-1273.815 (n = 50) or mRNA-1273.231 (n = 51); median intervals (interquartile range) from prior BA.4/BA.5 bivalent doses were 8.2 (8.1-8.3) and 8.3 (8.1-8.4) months, respectively. Fold increases in neutralizing antibody (nAb) against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants from prebooster nAb levels were numerically higher against XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, EG.5.1, BA.2.86, and JN.1 than BA.4/BA.5, BQ.1.1, or D614G on day 29. Monovalent vaccine also cross-neutralized FL.1.5.1, EG.5.1, BA.2.86, HK.3.1, HV.1, and JN.1 variants in a participant subset (n = 20) 15 days after vaccination. Reactogenicity was similar to that of mRNA-1273 vaccines.
Conclusions: XBB.1.5-containing mRNA-1273 vaccines elicit robust, diverse nAb responses against more recent SARS-CoV-2 variants, including JN.1, supporting the XBB.1.5-spike update for COVID-19 vaccines.
Keywords: COVID-19; JN.1; Omicron XBB.1.5; SARS-CoV-2 variants; mRNA vaccine.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest . S. C., N. M., B. G., D. K. E., K. W., A. N., D. L., L. E. A., J. F., W. D., J. M. M., and R. D. are employees of Moderna and may hold stock/stock options in the company. J. E. T. is a Moderna consultant. D. C. M. reports funding from Moderna for pseudovirus neutralization assays performed in the study. L. R. B. is a co–primary principal investigator of the COVE trial, funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and conducted in conjunction with Moderna. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee June 28, 2022 meeting. https://www.fda.gov/advisory-committees/advisory-committee-calendar/vacc.... Accessed 17 June 2023.
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. Updated COVID-19 vaccines for use in the United States beginning in fall 2023. https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/updated-covid-19-vaccines-u.... Accessed 17 June 2023.
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA recommends inclusion of Omicron BA.4/5 component for COVID-19 vaccine booster doses. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda.... Accessed 22 July 2022.
-
- CoVariants. Overview of variants/mutations. https://covariants.org/variants. Accessed 18 August 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

