Mass Azithromycin Distribution to Prevent Child Mortality in Burkina Faso: The CHAT Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38349371
- PMCID: PMC10865159
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.27393
Mass Azithromycin Distribution to Prevent Child Mortality in Burkina Faso: The CHAT Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Repeated mass distribution of azithromycin has been shown to reduce childhood mortality by 14% in sub-Saharan Africa. However, the estimated effect varied by location, suggesting that the intervention may not be effective in different geographical areas, time periods, or conditions.
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of twice-yearly azithromycin to reduce mortality in children in the presence of seasonal malaria chemoprevention.
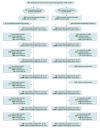
Design, setting, and participants: This cluster randomized placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of single-dose azithromycin for prevention of all-cause childhood mortality included 341 communities in the Nouna district in rural northwestern Burkina Faso. Participants were children aged 1 to 59 months living in the study communities.
Interventions: Communities were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive oral azithromycin or placebo distribution. Children aged 1 to 59 months were offered single-dose treatment twice yearly for 3 years (6 distributions) from August 2019 to February 2023.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was all-cause childhood mortality, measured during a twice-yearly enumerative census.
Results: A total of 34 399 children (mean [SD] age, 25.2 [18] months) in the azithromycin group and 33 847 children (mean [SD] age, 25.6 [18] months) in the placebo group were included. A mean (SD) of 90.1% (16.0%) of the censused children received the scheduled study drug in the azithromycin group and 89.8% (17.1%) received the scheduled study drug in the placebo group. In the azithromycin group, 498 deaths were recorded over 60 592 person-years (8.2 deaths/1000 person-years). In the placebo group, 588 deaths were recorded over 58 547 person-years (10.0 deaths/1000 person-years). The incidence rate ratio for mortality was 0.82 (95% CI, 0.67-1.02; P = .07) in the azithromycin group compared with the placebo group. The incidence rate ratio was 0.99 (95% CI, 0.72-1.36) in those aged 1 to 11 months, 0.92 (95% CI, 0.67-1.27) in those aged 12 to 23 months, and 0.73 (95% CI, 0.57-0.94) in those aged 24 to 59 months.
Conclusions and relevance: Mortality in children (aged 1-59 months) was lower with biannual mass azithromycin distribution in a setting in which seasonal malaria chemoprevention was also being distributed, but the difference was not statistically significant. The study may have been underpowered to detect a clinically relevant difference.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03676764.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Azithromycin for Prevention of Mortality in African Children: More Data, More Questions.JAMA. 2024 Feb 13;331(6):475-476. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.27329. JAMA. 2024. PMID: 38349381 No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO Guideline on Mass Drug Administration of Azithromycin to Children Under Five Years of Age to Promote Child Survival. World Health Organization ; 2020. - PubMed
-
- Keenan JD, Arzika AM, Maliki R, et al. ; MORDOR-Niger Study Group . Cause-specific mortality of children younger than 5 years in communities receiving biannual mass azithromycin treatment in Niger: verbal autopsy results from a cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet Glob Health. 2020;8(2):e288-e295. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30540-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

