Advancing Cardiomyocyte Maturation: Current Strategies and Promising Conductive Polymer-Based Approaches
- PMID: 38349615
- PMCID: PMC11468390
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202303288
Advancing Cardiomyocyte Maturation: Current Strategies and Promising Conductive Polymer-Based Approaches
Abstract
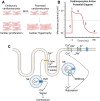
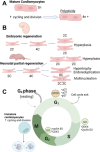
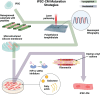
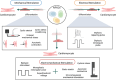
Cardiovascular diseases are a leading cause of mortality and pose a significant burden on healthcare systems worldwide. Despite remarkable progress in medical research, the development of effective cardiovascular drugs has been hindered by high failure rates and escalating costs. One contributing factor is the limited availability of mature cardiomyocytes (CMs) for accurate disease modeling and drug screening. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived CMs offer a promising source of CMs; however, their immature phenotype presents challenges in translational applications. This review focuses on the road to achieving mature CMs by summarizing the major differences between immature and mature CMs, discussing the importance of adult-like CMs for drug discovery, highlighting the limitations of current strategies, and exploring potential solutions using electro-mechano active polymer-based scaffolds based on conductive polymers. However, critical considerations such as the trade-off between 3D systems and nutrient exchange, biocompatibility, degradation, cell adhesion, longevity, and integration into wider systems must be carefully evaluated. Continued advancements in these areas will contribute to a better understanding of cardiac diseases, improved drug discovery, and the development of personalized treatment strategies for patients with cardiovascular disorders.
Keywords: cardiomyocyte maturation; cardiovascular research; conductive polymers; human induced pluripotent stem cells; physiological stimuli.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Healthcare Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Maturation of human cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC-CMs) on polycaprolactone and polyurethane nanofibrous mats.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 5;14(1):12975. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63905-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38839879 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Cardiovascular Diseases with hiPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes in 2D and 3D Cultures.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 11;21(9):3404. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093404. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32403456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-mediated maturation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes: Towards a better model for cardiotoxicity?Food Chem Toxicol. 2016 Dec;98(Pt A):17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.05.025. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Food Chem Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27265266 Review.
-
Cell number per spheroid and electrical conductivity of nanowires influence the function of silicon nanowired human cardiac spheroids.Acta Biomater. 2017 Mar 15;51:495-504. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.029. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28087483 Free PMC article.
-
Maturation of Cardiomyocytes Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells: Current Strategies and Limitations.Mol Cells. 2018 Jul 31;41(7):613-621. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2018.0143. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Mol Cells. 2018. PMID: 29890820 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Current State of Realistic Heart Models for Disease Modelling and Cardiotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 24;25(17):9186. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179186. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioprinting approaches in cardiac tissue engineering to reproduce blood-pumping heart function.iScience. 2024 Dec 20;28(1):111664. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111664. eCollection 2025 Jan 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39868032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conductive biological materials for in vitro models: properties and sustainability implications.In Vitro Model. 2025 Apr 24;4(2):89-110. doi: 10.1007/s44164-025-00088-5. eCollection 2025 Aug. In Vitro Model. 2025. PMID: 40708814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cho S., Discher D. E., Leong K. W., Vunjak‐Novakovic G., Wu J. C., Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 1064. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh P., Azam S., Jonkman M., Karim A., Shamrat F. M. J. M., Ignatious E., Shultana S., Beeravolu A. R., De Boer F., IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19304.
-
- Timmis A., Vardas P., Townsend N., Torbica A., Katus H., De Smedt D., Gale C. P., Maggioni A. P., Petersen S. E., Huculeci R., Kazakiewicz D., de Benito Rubio V., Ignatiuk B., Raisi‐Estabragh Z., Pawlak A., Karagiannidis E., Treskes R., Gaita D., Beltrame J. F., McConnachie A., Bardinet I., Graham I., Flather M., Elliott P., Mossialos E. A., Weidinger F., Achenbach S., Mimoza L., Artan G., Aurel D., et al., Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 716. - PubMed
-
- Dunbar S. B., Khavjou O. A., Bakas T., Hunt G., Kirch R. A., Leib A. R., Morrison R. S., Poehler D. C., Roger V. L., Whitsel L. P., Circulation 2018, 137, e558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

