Nanomaterials Regulate Bacterial Quorum Sensing: Applications, Mechanisms, and Optimization Strategies
- PMID: 38350718
- PMCID: PMC11022734
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202306070
Nanomaterials Regulate Bacterial Quorum Sensing: Applications, Mechanisms, and Optimization Strategies
Abstract
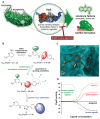
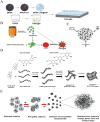
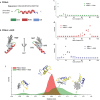
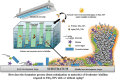
Anti-virulence therapy that interferes with bacterial communication, known as "quorum sensing (QS)", is a promising strategy for circumventing bacterial resistance. Using nanomaterials to regulate bacterial QS in anti-virulence therapy has attracted much attention, which is mainly attributed to unique physicochemical properties and excellent designability of nanomaterials. However, bacterial QS is a dynamic and multistep process, and there are significant differences in the specific regulatory mechanisms and related influencing factors of nanomaterials in different steps of the QS process. An in-depth understanding of the specific regulatory mechanisms and related influencing factors of nanomaterials in each step can significantly optimize QS regulatory activity and enhance the development of novel nanomaterials with better comprehensive performance. Therefore, this review focuses on the mechanisms by which nanomaterials regulate bacterial QS in the signal supply (including signal synthesis, secretion, and accumulation) and signal transduction cascade (including signal perception and response) processes. Moreover, based on the two key influencing factors (i.e., the nanomaterial itself and the environment), optimization strategies to enhance the QS regulatory activity are comprehensively summarized. Collectively, applying nanomaterials to regulate bacterial QS is a promising strategy for anti-virulence therapy. This review provides reference and inspiration for further research on the anti-virulence application of nanomaterials.
Keywords: antibacterial; anti‐virulence therapy; drug resistance; nanomaterials; optimization strategies; quorum sensing.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Contribution of quorum sensing to virulence and antibiotic resistance in zoonotic bacteria.Biotechnol Adv. 2022 Oct;59:107965. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.107965. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Biotechnol Adv. 2022. PMID: 35487393 Review.
-
Interactions between quorum sensing/quorum quenching and virulence genes may affect coral health by regulating symbiotic bacterial community.Environ Res. 2023 Dec 1;238(Pt 2):117221. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117221. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37775014
-
Unveiling the hidden language of bacteria: anti-quorum sensing strategies for gram-negative bacteria infection control.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Feb 27;206(3):124. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-03900-0. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38409503 Review.
-
Evidence for Complex Interplay between Quorum Sensing and Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0126922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01269-22. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36314960 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Aspects of the Functioning of Pathogenic Bacteria Biofilm Based on Quorum Sensing (QS) Signal-Response System and Innovative Non-Antibiotic Strategies for Their Elimination.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 24;25(5):2655. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052655. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473900 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori Detection Based on Synergistic Electromagnetic and Chemical Enhancement of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering in 3D Hotspot-Activated Gold Nanorods/Nano Mica Platelets/ZnO Quantum Dots.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jul;12(28):e2503562. doi: 10.1002/advs.202503562. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40265978 Free PMC article.
-
How Nanoparticles Help in Combating Chronic Wound Biofilms Infection?Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Nov 15;19:11883-11921. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S484473. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39563901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteria-Inspired Synthesis of Silver-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanocomposites: A Novel Synergistic Approach in Controlling Biofilm and Quorum-Sensing-Regulated Virulence Factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Jan 9;14(1):59. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010059. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858345 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotherapies based on bacterial metabolism: Mechanisms, design and application.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 18;34:102117. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102117. eCollection 2025 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40735698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanozyme-Based Strategies against Bone Infection.Research (Wash D C). 2025 Feb 11;8:0605. doi: 10.34133/research.0605. eCollection 2025. Research (Wash D C). 2025. PMID: 39935691 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 81701026/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2016YFC1102601/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 822QN449/Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021QNXM02/National Natural Science Fund Cultivating 530 Project of Hainan General Hospital
- QN202012/Courtyard's Level Program of Hainan General Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
