Green-synthesized silver nanoparticles from Zingiber officinale extract: antioxidant potential, biocompatibility, anti-LOX properties, and in silico analysis
- PMID: 38350963
- PMCID: PMC10863109
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-024-04381-w
Green-synthesized silver nanoparticles from Zingiber officinale extract: antioxidant potential, biocompatibility, anti-LOX properties, and in silico analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Zingiber officinale extract has emerged as a compelling candidate for green synthesis of nanoparticles, offering diverse applications across medicine, cosmetics, and nutrition. This study delves into the investigation of in vitro toxicity and explores the biomedical utility of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles derived from ginger extract (GE-AgNPs).
Methods: We employed established protocols to evaluate in vitro aspects such as antioxidant capacity, anti-inflammatory potential, and biocompatibility of GE-AgNPs. Additionally, molecular docking was employed to assess their anti-lipoxygenase (anti-LOX) activity.
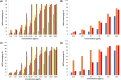
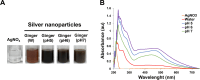
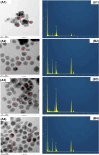
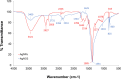
Results: Our findings highlight that the extraction of ginger extract at a pH of 6, utilizing a cosolvent blend of ethanol and ethyl acetate in a 1:1 ratio, yields heightened antioxidant capacity attributed to its rich phenolic and flavonoid content. In the context of silver nanoparticle synthesis, pH 6 extraction yields the highest quantity of nanoparticles, characterized by an average size of 32.64 ± 1.65 nm. Of particular significance, GE-AgNPs (at pH 6) demonstrated remarkable efficacy in scavenging free radicals, as evidenced by an IC50 value of 6.83 ± 0.47 µg/mL. The results from the anti-LOX experiment indicate that GE-AgNPs, at a concentration of 10 µg/mL, can inhibit LOX activity by 25%, outperforming ginger extract which inhibits LOX by 17-18%. Notably, clionasterol exhibited higher binding energy and enhanced stability (-8.9 kcal/mol) compared to nordihydroguaiaretic acid. Furthermore, a cell viability study confirmed the safety of GE-AgNPs at a concentration of 17.52 ± 7.00 µg/mL against the L929 cell line.
Conclusion: These comprehensive findings underscore the significant biomedical advantages of GE-AgNPs and emphasize their potential incorporation into cosmetic products at a maximum concentration of 10 µg/mL.
Keywords: Anti-LOX; Antioxidant; Biocompatibility; Silver nanoparticles; Zingiber officinale.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their antioxidant activity and potential catalytic reduction activities with Direct Blue 15 or Direct Orange 26.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 25;17(8):e0271408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271408. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36006900 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles from Rhizophora apiculata and Studies on Their Wound Healing, Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Cytotoxic Activity.Molecules. 2022 Sep 24;27(19):6306. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196306. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234841 Free PMC article.
-
Green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Zingiber officinale root extract and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles against food pathogens.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2014 Oct;37(10):1935-43. doi: 10.1007/s00449-014-1169-6. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2014. PMID: 24668029
-
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles; A Sustainable Approach with Diverse Applications.Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Dec 21;39:e20230007. doi: 10.62958/j.cjap.2023.007. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38763765 Review.
-
A Brief Overview on Antioxidant Activity Determination of Silver Nanoparticles.Molecules. 2020 Jul 13;25(14):3191. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143191. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32668682 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative efficacy of Knema retusa extract delivery via PEG-b-PCL, niosome, and their combination against Acanthamoeba triangularis genotype T4: characterization, inhibition, anti-adhesion, and cytotoxic activity.PeerJ. 2024 Nov 15;12:e18452. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18452. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39559326 Free PMC article.
-
A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (SNPs) using plant extracts: a multifaceted approach in photocatalysis, environmental remediation, and biomedicine.RSC Adv. 2025 Feb 6;15(5):3858-3903. doi: 10.1039/d4ra07519f. eCollection 2025 Jan 29. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 39917042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the antibacterial efficacy of combinations of Garcinia mangostana, Curcuma comosa, and Acanthus ebracteatus for acne vulgaris treatment: in Silico and in vitro validation.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jul 10;25(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04997-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40640786 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis and Characterization of Ginger-Derived Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant, Antibacterial, and Anticancer Activities.Plants (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;13(9):1255. doi: 10.3390/plants13091255. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38732470 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Synergistic Inhibition of Inflammatory and Antioxidant Potential: Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Analyses of Garcinia mangostana, Curcuma comosa, and Acanthus ebracteatus.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024 Sep 18;2024:8584015. doi: 10.1155/2024/8584015. eCollection 2024. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39328582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thipe VC, Karikachery AR, Çakılkaya P, Farooq U, Genedy HH, Kaeokhamloed N, Phan D-H, Rezwan R, Tezcan G, Roger E, et al. Green nanotechnology—An innovative pathway towards biocompatible and medically relevant gold nanoparticles. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol. 2022;70:103256. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103256. - DOI
-
- Mohammadinejad R, Karimi S, Iravani S, Varma RS. Plant-derived nanostructures: types and applications. J Green Chemistry. 2016;18(1):20–52. doi: 10.1039/C5GC01403D. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

