Visual Recovery Time in Patients with Ethambutol-induced Toxic Optic Neuropathy
- PMID: 38351490
- PMCID: PMC11016690
- DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2023.0095
Visual Recovery Time in Patients with Ethambutol-induced Toxic Optic Neuropathy
Abstract
Purpose: We aimed to investigate the visual recovery time in patients with ethambutol-induced toxic optic neuropathy (EON) and identify the factors associated with the visual recovery time.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we reviewed the medical records of 35 eyes from 35 patients with EON. Visual recovery was defined as a gain of three or more lines from the nadir.
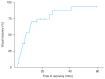
Results: Patients were observed following discontinuation of ethambutol (EMB), with the mean follow-up period of 21.0 ± 16.0 months. The visual acuity at nadir was logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution 1.4 ± 0.4, and the final visual acuity was logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution 0.6 ± 0.5. Twenty-seven eyes (77.1%) showed significant visual recovery. In Kaplan-Meier survival, the mean estimated time for visual recovery was 15.2 ± 3.0 months, and 50% of the patients experienced visual recovery at 8.3 ± 2.2 months following EMB discontinuation. Multivariate Cox regression analysis identified several significant risk factors for delayed visual recovery, including duration of EMB medication ≤6 months, period from symptom onset to EMB discontinuation >14 days, and baseline peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness >98 μm.
Conclusions: Our study indicated a mean time of visual recovery of 15 months for EON cases. Therefore, patients diagnosed with EON should be followed up for more than 1 to 2 years to evaluate their visual recovery. Delayed EMB discontinuation, short duration of EMB use, and initial peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickening were associated with delayed visual recovery. Therefore, patients taking EMB should be followed up regularly for early detection of EON and immediate discontinuation of EMB to prevent severe damage to the optic nerve.
Keywords: Ethambutol; Toxic optic neuropathy; Visual recovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Temporal evolution and factors influencing visual function and RNFL thickness in ethambutol-associated optic neuropathy.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Apr 23;30(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02573-9. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40269990 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal analysis of retinal nerve fiber layer and ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer thickness in ethambutol-induced optic neuropathy.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015 Dec;253(12):2293-9. doi: 10.1007/s00417-015-3150-8. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26344730
-
Ganglion Cell Layer and Inner Plexiform Layer as Predictors of Vision Recovery in Ethambutol-Induced Optic Neuropathy: A Longitudinal OCT Analysis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Apr 1;59(5):2104-2109. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22988. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29677374
-
Ethambutol-induced optic neuropathy: Functional and structural changes in the retina and optic nerve.Semin Ophthalmol. 2022 Aug;37(6):730-739. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2022.2085517. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Semin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35699333 Review.
-
Ethambutol optic neuropathy.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2017 Nov;28(6):545-551. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000416. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28759559 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal evolution and factors influencing visual function and RNFL thickness in ethambutol-associated optic neuropathy.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Apr 23;30(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02573-9. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40269990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee EJ, Kim SJ, Choung HK, et al. Incidence and clinical features of ethambutol-induced optic neuropathy in Korea. J Neuroophthalmol. 2008;28:269–77. - PubMed
-
- Chen HY, Lai SW, Muo CH, et al. Ethambutol-induced optic neuropathy: a nationwide population-based study from Taiwan. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012;96:1368–71. - PubMed
-
- Leibold JE. The ocular toxicity of ethambutol and its relation to dose. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966;135:904–9. - PubMed
-
- Bobrowitz ID. Ethambutol in the retreatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966;135:796–822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous