Endobronchial ultrasound: A novel screening test for pulmonary hypertension prior to major pulmonary surgery
- PMID: 38352000
- PMCID: PMC10859667
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjtc.2023.10.030
Endobronchial ultrasound: A novel screening test for pulmonary hypertension prior to major pulmonary surgery
Abstract
Objectives: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is an important physiologic variable in the assessment of patients undergoing major thoracic operations but all too often neglected because of the need for right heart catheterization (RHC) due to the inaccuracy of transthoracic echocardiography. Patients with lung cancer often require endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) as part of the staging of the cancer. We sought to investigate whether EBUS can be used to screen these patients for PH.
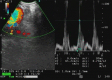
Methods: Patients undergoing a major thoracic operation requiring EBUS for staging were included prospectively in the study. All patients had also a RHC (gold standard). We aimed to compare the pulmonary artery pressure measurements by EBUS with the RHC values.
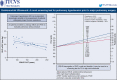
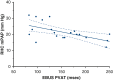
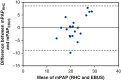
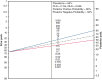
Results: A total of 20 patients were enrolled in the study. The prevalence of abnormal pulmonary artery pressure was 65% based on RHC. All patients underwent measurement of the pulmonary vascular acceleration time (PVAT) by EBUS with no adverse events. Linear regression analysis comparing PVAT and RHC showed a correlation (r = -0.059, -0.010 to -0.018, P = .007). A receiver operator characteristic curve (area under the curve = 0.736) was used to find the optimal PVAT threshold (140 milliseconds) to predict PH; this was used to calculate a positive and negative likelihood ratio following a positive diagnosis of 2.154 and 0.538, respectively.
Conclusions: EBUS interrogation of pulmonary artery hemodynamic is safe and feasible. EBUS may be used as a screening test for PH in high-risk individuals.
Keywords: endobronchial ultrasound; high risk lung resection; preoperative screening; pulmonary hypertension.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.F.C. has received research grants from Siemens and Olympus, and he is paid consultant for Intuitive Surgical, Siemens, and Olympus. All other authors reported no conflicts of interest. The Journal policy requires editors and reviewers to disclose conflicts of interest and to decline handling or reviewing manuscripts for which they may have a conflict of interest. The editors and reviewers of this article have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlation between Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measured by Echocardiography and Right Heart Catheterization in Patients with Rheumatic Mitral Valve Stenosis (A Prospective Study).Echocardiography. 2016 Jan;33(1):7-13. doi: 10.1111/echo.13000. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Echocardiography. 2016. PMID: 26096532
-
Assessment of Pulmonary Hypertension in Lung Transplantation Candidates: Correlation of Doppler Echocardiography With Right Heart Catheterization.Transplant Proc. 2016 Oct;48(8):2797-2802. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2016.06.055. Transplant Proc. 2016. PMID: 27788820
-
Aetiological distribution of pulmonary hypertension and the value of transthoracic echocardiography screening in the respiratory department: A retrospective analysis from China.Clin Respir J. 2023 Jun;17(6):536-547. doi: 10.1111/crj.13623. Epub 2023 May 4. Clin Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37141914 Free PMC article.
-
Right Heart Catheterization (RHC): A Comprehensive Review of Provocation Tests and Hepatic Hemodynamics in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension (PH).Curr Probl Cardiol. 2022 Dec;47(12):101351. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101351. Epub 2022 Aug 7. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35948196 Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of endobronchial ultrasound-transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) for mediastinal lymph node staging of lung cancer.Mediastinum. 2021 Jun 25;5:15. doi: 10.21037/med-21-2. eCollection 2021. Mediastinum. 2021. PMID: 35118321 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dauriat G., LePavec J., Pradere P., Savale L., Fabre D., Fadel E. Our current understanding of and approach to the management of lung cancer with pulmonary hypertension. Exp Rev Respir Med. 2021;15:373–384. - PubMed
-
- Criner G.J., Cordova F., Sternberg A.L., Martinez F.J. The National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184:763–770. - PubMed
-
- Rol N., Happe C., Belien J.A., de Man F.S., Westerhof N., Vonk-Noordegraaf A., et al. Vascular remodelling in the pulmonary circulation after major lung resection. Eur Respir J. 2017;50 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

