Autonomous Robotic Surgery: Has the Future Arrived?
- PMID: 38352080
- PMCID: PMC10862530
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.52243
Autonomous Robotic Surgery: Has the Future Arrived?
Abstract
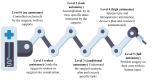
Autonomous robotic surgery represents a pioneering field dedicated to the integration of robotic systems with varying degrees of autonomy for the execution of surgical procedures. This paradigm shift is made possible by the progressive integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into the realm of surgical interventions. While the majority of autonomous robotic systems remain in the experimental phase, a notable subset has successfully transitioned into clinical applications. Noteworthy procedures, such as venipuncture, hair implantations, intestinal anastomosis, total knee replacement, cochlear implant, radiosurgery, and knot tying, among others, exemplify the current capabilities of autonomous surgical systems. This review endeavors to comprehensively address facets of autonomous robotic surgery, commencing with a concise elucidation of fundamental concepts and traversing the pivotal milestones in the historical evolution of robotic surgery. This historical trajectory underscores the incremental assimilation of autonomous systems into surgical practices. This review aims to address topics related to autonomous robotic surgery, starting with a description of fundamental concepts and going through the milestones in robotic surgery history that also show the gradual incorporations of autonomous systems. It also includes a discussion of the key benefits and risks of this technology, the degrees of autonomy in surgical robots, their limitations, the current legal regulations governing their usage, and the main ethical concerns inherent to their nature.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; autonomous robotic surgery; clinical applications; degrees of autonomy; ethical concerns; legal regulations; robotic surgery milestones.
Copyright © 2024, Rivero-Moreno et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Supervised autonomous robotic soft tissue surgery. Shademan A, Decker RS, Opfermann JD, Leonard S, Krieger A, Kim PC. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:337. - PubMed
-
- Introduction to artificial intelligence in medicine. Mintz Y, Brodie R. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2019;28:73–81. - PubMed
-
- ChatGPT's contributions to the evolution of neurosurgical practice and education: a systematic review of benefits, concerns and limitations. Bečulić H, Begagić E, Skomorac R, Mašović A, Selimović E, Pojskić M. Med Glas (Zenica) 2024;21 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources