This is a preprint.
Development of non-sedating antischistosomal benzodiazepines
- PMID: 38352313
- PMCID: PMC10862742
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.26.577323
Development of non-sedating antischistosomal benzodiazepines
Abstract
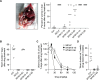
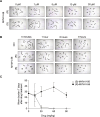
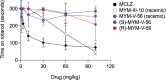
The neglected tropical disease schistosomiasis infects over 200 million people worldwide and is treated with just one broad spectrum antiparasitic drug (praziquantel). Alternative drugs are needed in the event of emerging praziquantel resistance or treatment failure. One promising lead that has shown efficacy in animal models and a human clinical trial is the benzodiazepine meclonazepam, discovered by Roche in the 1970's. Meclonazepam was not brought to market because of dose-limiting sedative side effects. However, the human target of meclonazepam that causes sedation (GABAARs) are not orthologous to the parasite targets that cause worm death. Therefore, we were interested in whether the structure of meclonazepam could be modified to produce antiparasitic benzodiazepines that do not cause host sedation. We synthesized 18 meclonazepam derivatives with modifications at different positions on the benzodiazepine ring system and tested them for in vitro antiparasitic activity. This identified five compounds that progressed to in vivo screening in a murine model, two of which cured parasite infections with comparable potency to meclonazepam. When these two compounds were administered to mice that were run on the rotarod test, both were less sedating than meclonazepam. These findings demonstrate the proof of concept that meclonazepam analogs can be designed with an improved therapeutic index, and point to the C3 position of the benzodiazepine ring system as a logical site for further structure-activity exploration to further optimize this chemical series.
Figures




References
-
- Lo NC, Bezerra FSM, Colley DG, Fleming FM, Homeida M, Kabatereine N, Kabole FM, King CH, Mafe MA, Midzi N, Mutapi F, Mwanga JR, Ramzy RMR, Satrija F, Stothard JR, Traoré MS, Webster JP, Utzinger J, Zhou X-N, Danso-Appiah A, Eusebi P, Loker ES, Obonyo CO, Quansah R, Liang S, Vaillant M, Murad MH, Hagan P, Garba A. 2022. Review of 2022 WHO guidelines on the control and elimination of schistosomiasis. Lancet Infect Dis 22:e327–e335. - PubMed
-
- Berger DJ, Crellen T, Lamberton PHL, Allan F, Tracey A, Noonan JD, Kabatereine NB, Tukahebwa EM, Adriko M, Holroyd N, Webster JP, Berriman M, Cotton JA. 2021. Whole-genome sequencing of Schistosoma mansoni reveals extensive diversity with limited selection despite mass drug administration. Nat Commun 12:4776. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ismail MM, Taha SA, Farghaly AM, el-Azony AS. 1994. Laboratory induced resistance to praziquantel in experimental schistosomiasis. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 24:685–695. - PubMed
-
- Fallon PG, Doenhoff MJ. 1995. Drug-resistant schistosomiasis: resistance to praziquantel and oxamniquine induced in Schistosoma mansoni in mice is drug specific. Am J Trop Med Hyg 53:61–62. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
