This is a preprint.
Neurotrophic factor Neuritin modulates T cell electrical and metabolic state for the balance of tolerance and immunity
- PMID: 38352414
- PMCID: PMC10862906
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.31.578284
Neurotrophic factor Neuritin modulates T cell electrical and metabolic state for the balance of tolerance and immunity
Update in
-
Neurotrophic factor Neuritin modulates T cell electrical and metabolic state for the balance of tolerance and immunity.Elife. 2024 Nov 20;13:RP96812. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96812. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39565188 Free PMC article.
Abstract
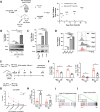
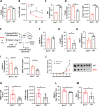
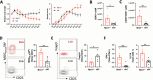
The adaptive T cell response is accompanied by continuous rewiring of the T cell's electric and metabolic state. Ion channels and nutrient transporters integrate bioelectric and biochemical signals from the environment, setting cellular electric and metabolic states. Divergent electric and metabolic states contribute to T cell immunity or tolerance. Here, we report that neuritin (Nrn1) contributes to tolerance development by modulating regulatory and effector T cell function. Nrn1 expression in regulatory T cells promotes its expansion and suppression function, while expression in the T effector cell dampens its inflammatory response. Nrn1 deficiency causes dysregulation of ion channel and nutrient transporter expression in Treg and effector T cells, resulting in divergent metabolic outcomes and impacting autoimmune disease progression and recovery. These findings identify a novel immune function of the neurotrophic factor Nrn1 in regulating the T cell metabolic state in a cell context-dependent manner and modulating the outcome of an immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: C.D. is a co-inventor on patents licensed from JHU to BMS and Janssen and is currently an employee of Janssen Research. D.M.P. is a consultant for Compugen, Shattuck Labs, WindMIL, Tempest, Immunai, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amgen, Janssen, Astellas, Rockspring Capital, Immunomic, and Dracen; owns founders equity in ManaT Bio Inc., WindMIL, Trex, Jounce, Enara, Tizona, Tieza, and RAPT; and receives research funding from Compugen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Enara. All other authors do not have conflicting financial interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
