This is a preprint.
Programmable RNA writing with trans-splicing
- PMID: 38352602
- PMCID: PMC10862893
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.31.578223
Programmable RNA writing with trans-splicing
Abstract
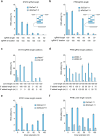
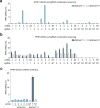
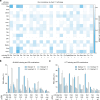
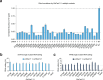
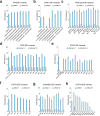
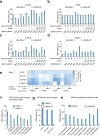
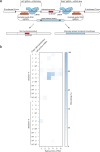
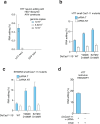
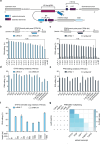
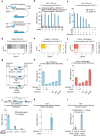
RNA editing offers the opportunity to introduce either stable or transient modifications to nucleic acid sequence without permanent off-target effects, but installation of arbitrary edits into the transcriptome is currently infeasible. Here, we describe Programmable RNA Editing & Cleavage for Insertion, Substitution, and Erasure (PRECISE), a versatile RNA editing method for writing RNA of arbitrary length and sequence into existing pre-mRNAs via 5' or 3' trans-splicing. In trans-splicing, an exogenous template is introduced to compete with the endogenous pre-mRNA, allowing for replacement of upstream or downstream exon sequence. Using Cas7-11 cleavage of pre-mRNAs to bias towards editing outcomes, we boost the efficiency of RNA trans-splicing by 10-100 fold, achieving editing rates between 5-50% and 85% on endogenous and reporter transcripts, respectively, while maintaining high-fidelity. We demonstrate PRECISE editing across 11 distinct endogenous transcripts of widely varying expression levels, showcasing more than 50 types of edits, including all 12 possible transversions and transitions, insertions ranging from 1 to 1,863 nucleotides, and deletions. We show high efficiency replacement of exon 4 of MECP2, addressing most mutations that drive the Rett Syndrome; editing of SHANK3 transcripts, a gene involved in Autism; and replacement of exon 1 of HTT, removing the hallmark repeat expansions of Huntington's disease. Whole transcriptome sequencing reveals the high precision of PRECISE editing and lack of off-target trans-splicing activity. Furthermore, we combine payload engineering and ribozymes for protein-free, high-efficiency trans-splicing, with demonstrated efficiency in editing HTT exon 1 via AAV delivery. We show that the high activity of PRECISE editing enables editing in non-dividing neurons and patient-derived Huntington's disease fibroblasts. PRECISE editing markedly broadens the scope of genetic editing, is straightforward to deliver over existing gene editing tools like prime editing, lacks permanent off-targets, and can enable any type of genetic edit large or small, including edits not otherwise possible with existing RNA base editors, widening the spectrum of addressable diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A patent application has been filed related to this work. J.S.G. and O.O.A. are co-founders of Sherlock Biosciences, Proof Diagnostics, Tome Biosciences, and Doppler Bio.
Figures





References
-
- Nishida K. et al. Targeted nucleotide editing using hybrid prokaryotic and vertebrate adaptive immune systems. Science 353, (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
