Assessment of Availability of Tracer Drugs and Basic Diagnostics at Public Primary Health Care Facilities in Ethiopia During COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 38352669
- PMCID: PMC10859737
- DOI: 10.4314/ejhs.v33i2.7S
Assessment of Availability of Tracer Drugs and Basic Diagnostics at Public Primary Health Care Facilities in Ethiopia During COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Background: The emergence of COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted the supply chain and stock of medicines and drugs across the globe. Tracer drugs are essential medicines that address the population's priority health problems. Thus, this study aimed to assess availability of tracer drugs and basic diagnostics at public primary health care facilities in Ethiopia.
Methods: Facility based cross-sectional study was employed in four regions and one city administration. The primary health care units (PHCUs) were purposively selected in consultation with respective regional health bureaus. Finally, 16 hospitals, 92 health centers and 344 health posts were included. This study adopted WHO's tool that was being used to rapidly assess the capacity of health facilities to maintain the provision of essential health services during the COVID-19. Descriptive analysis was done using frequency and percentage, and results were presented.
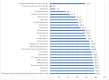
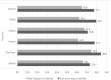
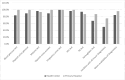
Results: The overall mean availability of tracer drugs in PHCUs was 77.6%. Only 2.8% of PHCUs have all tracer drugs. The mean availability of basic diagnostic at national level was 86.6% in PHUs except health posts where it was less. Health facilities with all basic diagnostic services was 53.7%. Of the total 344 health posts assessed, 71% were providing diagnostic testing for malaria using either laboratory equipment or rapid diagnostic test (RDT) while 43% provide urine test for the pregnancy.
Conclusion: This study shows availability of all tracer drugs in PHCUs in Ethiopia was extremely low. There was regional variation in availability of tracer drugs and basic diagnostics. It is very crucial to increase availability of tracer drugs and diagnostics. Drugs and diagnostic materials should be supplied according to the capacity and location of health facilities.
Keywords: Ethiopia; availability; basic diagnostics; primary health care units; tracer drugs.
© 2023 Abdurezak U., et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Communicable and Non-communicable Diseases Diagnosis and Treatment Service Availability at Primary Health Care Units During COVID-19 Outbreak in Ethiopia.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2023 Oct;33(Spec Iss 2):95-104. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v33i2.3S. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 38352666 Free PMC article.
-
Availability of essential, generic medicines before and during COVID-19 at selected public pharmaceutical supply agencies in Ethiopia: a comparative cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2024 Mar 4;14(3):e077545. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-077545. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38443082 Free PMC article.
-
Quality antenatal care services delivery at health facilities of Ethiopia, assessment of the structure/input of care setting.BMC Health Serv Res. 2020 Jun 1;20(1):485. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05372-6. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. PMID: 32487097 Free PMC article.
-
Health facilities readiness to provide comprehensive abortion care and factors associated with client satisfaction in Central Oromia Region, Ethiopia: a multilevel modeling approach.Reprod Health. 2023 May 11;20(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12978-023-01610-2. Reprod Health. 2023. PMID: 37170219 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liang T. Handbook of COVID-19 prevention and treatment. The first affiliated hospital, zhejiang university school of medicine Compiled According to Clinical Experience. 2020. p. 68.
-
- worldometer, author. COVID-19 CORONAVIRUS PANDEMIC [Internet] 2023. Aug 20, Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
