Inflammasome signaling is dispensable for ß-amyloid-induced neuropathology in preclinical models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 38352874
- PMCID: PMC10863058
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1323409
Inflammasome signaling is dispensable for ß-amyloid-induced neuropathology in preclinical models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder affecting memory and cognition. The disease is accompanied by an abnormal deposition of ß-amyloid plaques in the brain that contributes to neurodegeneration and is known to induce glial inflammation. Studies in the APP/PS1 mouse model of ß-amyloid-induced neuropathology have suggested a role for inflammasome activation in ß-amyloid-induced neuroinflammation and neuropathology.
Methods: Here, we evaluated the in vivo role of microglia-selective and full body inflammasome signalling in several mouse models of ß-amyloid-induced AD neuropathology.
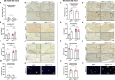
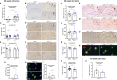
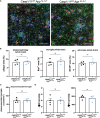
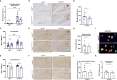
Results: Microglia-specific deletion of the inflammasome regulator A20 and inflammasome effector protease caspase-1 in the AppNL-G-F and APP/PS1 models failed to identify a prominent role for microglial inflammasome signalling in ß-amyloid-induced neuropathology. Moreover, global inflammasome inactivation through respectively full body deletion of caspases 1 and 11 in AppNL-G-F mice and Nlrp3 deletion in APP/PS1 mice also failed to modulate amyloid pathology and disease progression. In agreement, single-cell RNA sequencing did not reveal an important role for Nlrp3 signalling in driving microglial activation and the transition into disease-associated states, both during homeostasis and upon amyloid pathology.
Conclusion: Collectively, these results question a generalizable role for inflammasome activation in preclinical amyloid-only models of neuroinflammation.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; inflammasome; microglia; neuroinflammation; ß-amyloid.
Copyright © 2024 Srinivasan, Kancheva, De Ren, Saito, Jans, Boone, Vandendriessche, Paesmans, Maurin, Vandenbroucke, Hoste, Voet, Scheyltjens, Pavie, Lippens, Schwabenland, Prinz, Saido, Bottelbergs, Movahedi, Lamkanfi and van Loo.
Conflict of interest statement
SD, IP, HM, and AB are employed by Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. ML serves as a consultant for Ventyx Biosciences and Novo Nordisk outside of the submitted work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

